BY NOKUTHABA DLAMINI
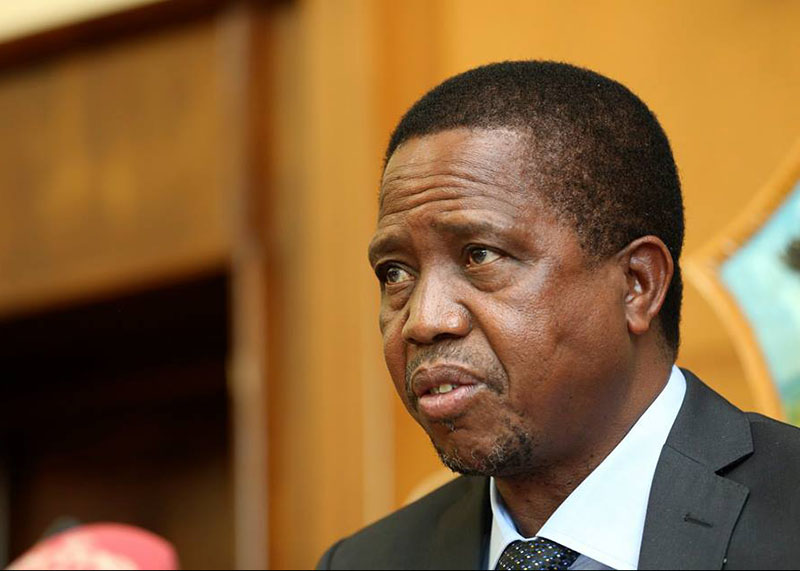
Zambian opposition leader Hakainde Hichilema has been declared winner of the country’s hotly contested presidential election, defeating the incumbent Edgar Lungu.
Justice Esau Chulu, Electoral Commission of Zambia chairperson, declared Hichelema the winner in the early hours of Monday with official results showing the wealthy businessman securing 2 810 757 votes against Lungu’s 1 814 201 votes.
Only one constituency out of the 156 was yet to report after vote counting for the August 12 presidential and parliamentary elections took longer than expected due to a high turnout.
“I therefore declare the said Hakainde Hichilema to be president-elect of the Republic of Zambia, Justice Chulu said in a televised address.
“The outstanding results are not likely to materially influence the overall results of this election,” he added.
“Therefore, the consolidated results are of 155 constituencies out of 156.’
The announcement sparked wild celebrations on the streets, but Lungu who was seeking a second full term after coming into power in 2015 is yet to concede defeat.
At the weekend, he declared that the elections were not free and fair because there were incidents of political violence in three provinces where supporters of his ruling Patriotic Front (PF) were targeted.
Hichelema, a former business executive and leader of the opposition United Party for National Development (UPND), won the presidency on his sixth attempt.
He becomes Zambia’s seventh president. In the previous elections, the UPND leader lost to Lungu by 100 000 votes.
In the run-up to the elections, the 64-year-old outgoing president’s popularity took a battering because of the rising cost of living and his increasing dictatorial tendencies.
Under his stewardship, the southern African country started choking from colossal debt, runaway inflation, corruption, and a weakening currency.
An Afrobarometer Sustainable Development Goals Scorecard for Zambia released in July showed that “the country is experiencing worsening poverty, hunger, and economic and ethnic inequalities compared to five years ago.”
Lungu’s government has also been accused of spending indiscipline at a time when the economy is suffering under the weight of a Covid-19 pandemic.
There was a 70 percent voter turnout in the elections and Hichilema enjoyed the support of other opposition parties.
Lungu and his PF began crying foul after less than half of the constituencies had reported their results.
Five opposition leaders, namely Harry Kalaba, Nevers Mumba, Fred Mmembe, Chishala Kateka, Sean Tembo and Trevor Mwamba immediately wrote to the embattled leader urging him to concede defeat.
The leaders said the PF leader cannot cry foul because he tried to use his incumbency to tilt the scales in his favour during the polls.
The UNDP said the claims that the elections were not free and fair were emanating from people “trying to throw out the entire election just to cling on to their jobs.”
Observers said Lungu had no choice, but to concede defeat as he was already isolated.
In terms of Zambia’s electoral laws, the defeated president must approach the Constitutional Court within seven days after a winner is announced if he wants to overturn the results.
International observer missions that included the European Union, African Union and Common Market for Eastern and Southern Africa declared the elections free and fair but condemned the sporadic violence.
The EU also criticised the restrictions on freedom of assembly and the abuse of state resources by the incumbent, who deployed the military on the streets on the eve of the polls.
Hichilema and his party were prevented from campaigning in several areas by security forces, who cited measures to control the spread of the coronavirus.

 Slider3 years ago
Slider3 years ago
 National4 years ago
National4 years ago
 Tourism and Environment4 years ago
Tourism and Environment4 years ago
 Special reports4 years ago
Special reports4 years ago
 Opinion4 years ago
Opinion4 years ago
 National4 years ago
National4 years ago
 National3 years ago
National3 years ago
 National3 years ago
National3 years ago