BY NOKUTHABA DLAMINI
In the small town of Bela-Bela, a quietly flourishing business is unfolding — one that turns wildlife into livelihood, education, and economic opportunity. On a humid afternoon, we walked into the operations of Estelle Nel Taxidermy (and its parent networks), where rows of beautiful animal mounts — from antelope horns to zebra skins, skulls to full-body trophies — line the walls.
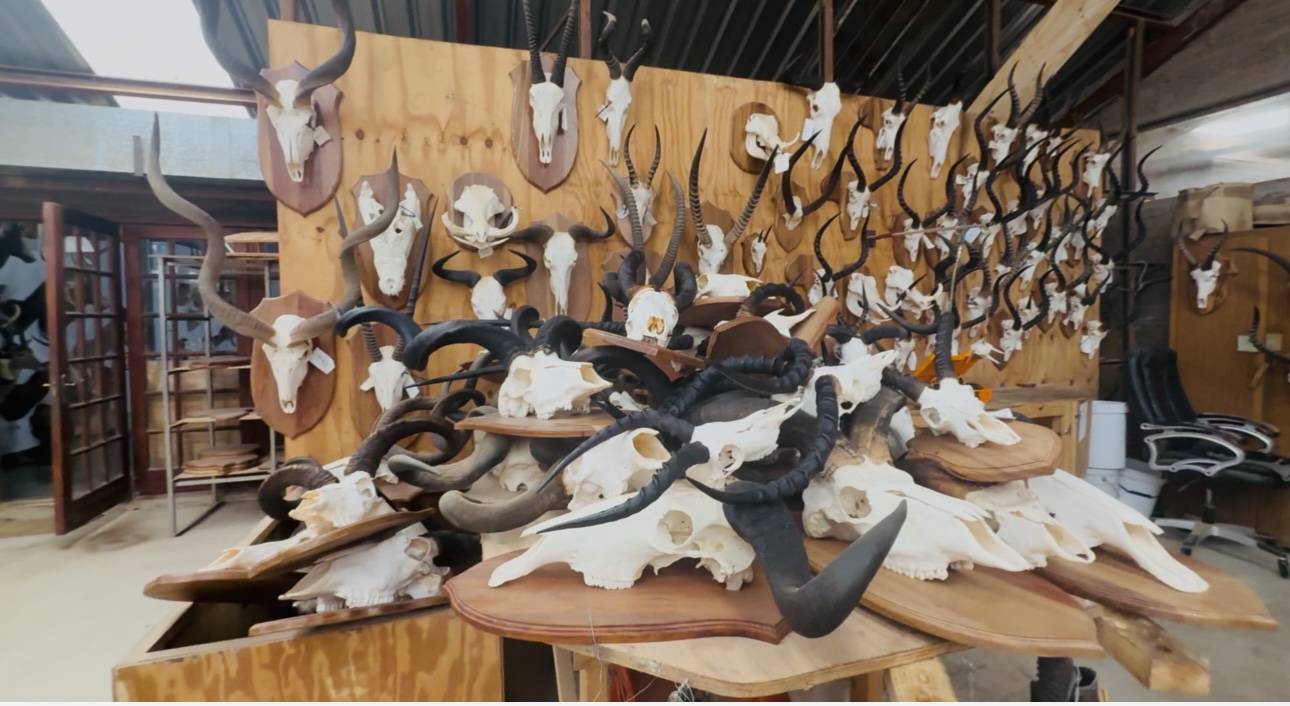

But beyond the busts and custom mounts lies a deeper purpose: this is not simply a display of hunting trophies. It is a system of sustainable use — where animals that die naturally or are hunted legally are completely utilised: meat, skin, horns, bones — nothing goes to waste, and everything acquires value.
As we discovered from our conversations, this network extends beyond taxidermy. Adjacent to the showrooms are processing facilities, butcheries, and game-meat wholesalers — all integral to transforming South Africa’s wild fauna into a formal, regulated, and sustainable economy.
“This is home” — an artisan’s vocation
I sat down with Melanie Viljoen, who serves as Export Secretary at Estelle Nel Taxidermy. Her voice was calm, resolute.
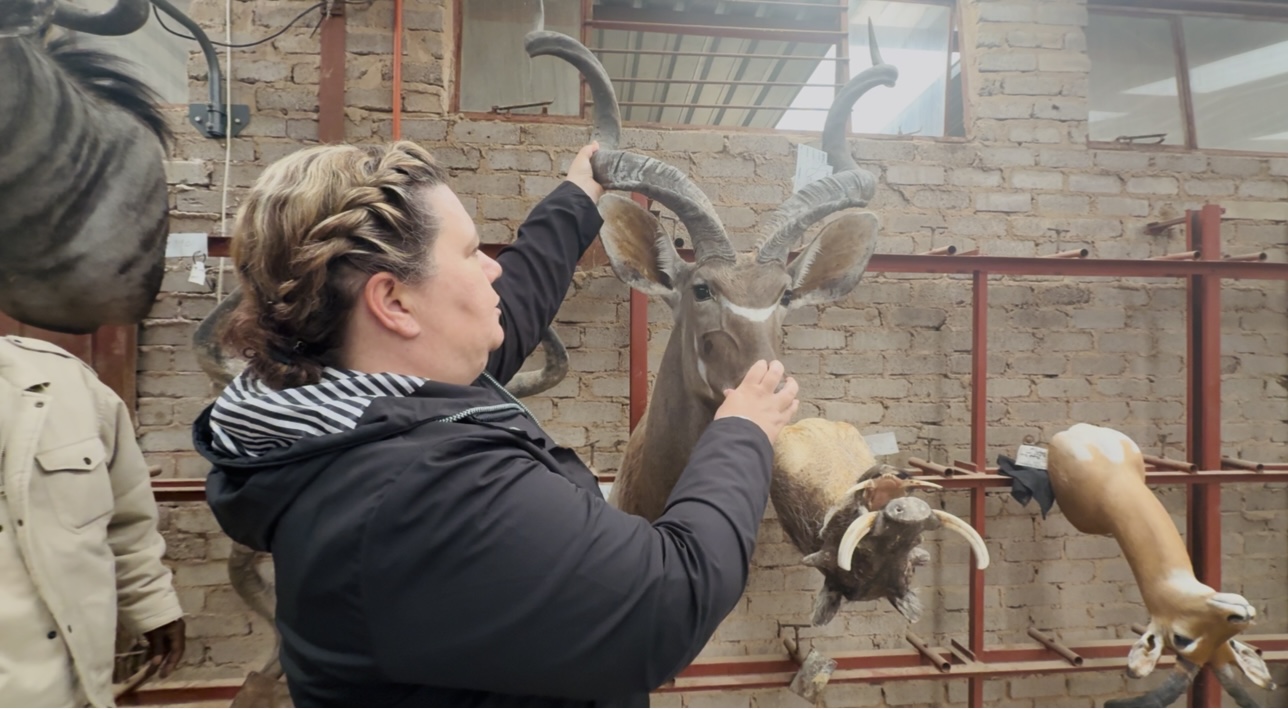

“For me, it’s like this is home and it’s something that I love to do. I love art. I studied art at school. I can’t think of anything else I’d rather do.”
She told us she’s been with the business for thirteen to fourteen years. Over that time she’s mastered a unique craft. “I’ve found my niche,” she said, “and I’m not going anywhere.”
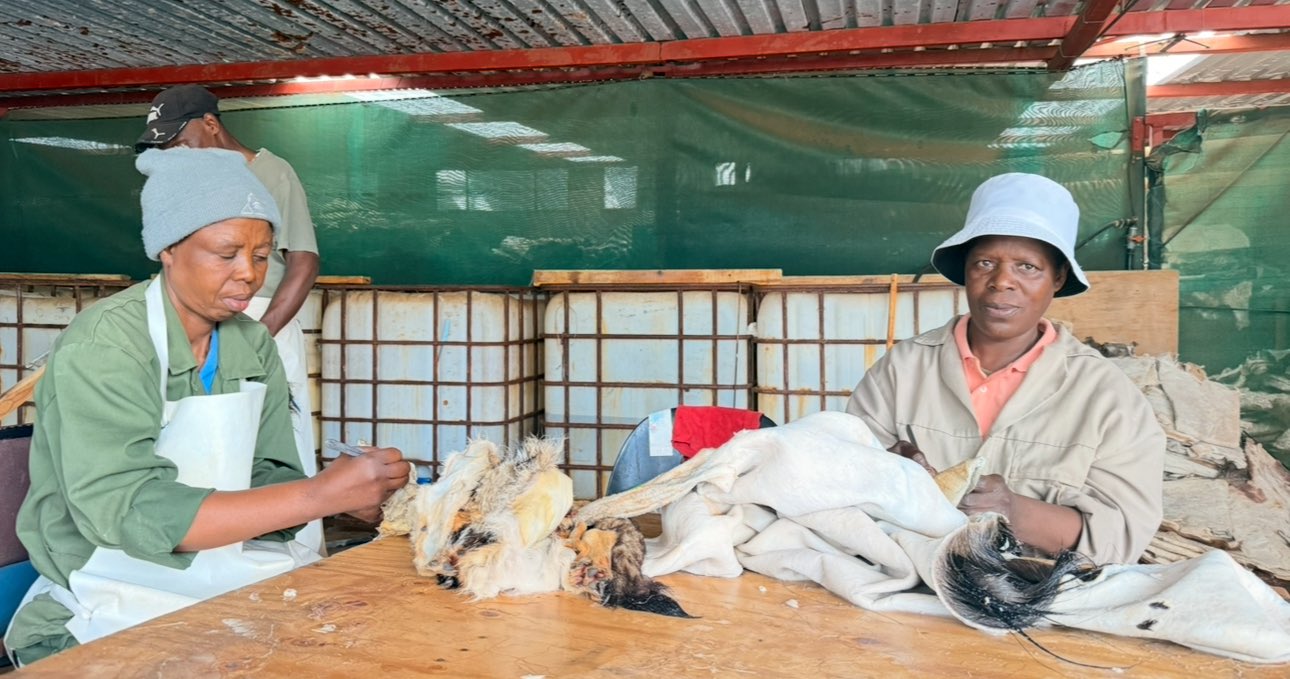
Melanie explained how the business flows: outfitters bring in international clients to hunt on private farms, then process the animals: trophy mounts for some, meat for others. Locals also bring animals — sometimes for trophies, sometimes just for meat. There is even “school-mount” work: smaller species, sometimes a mother and its young, carefully preserved — not just for hunters, but for children to touch and learn about wildlife up close.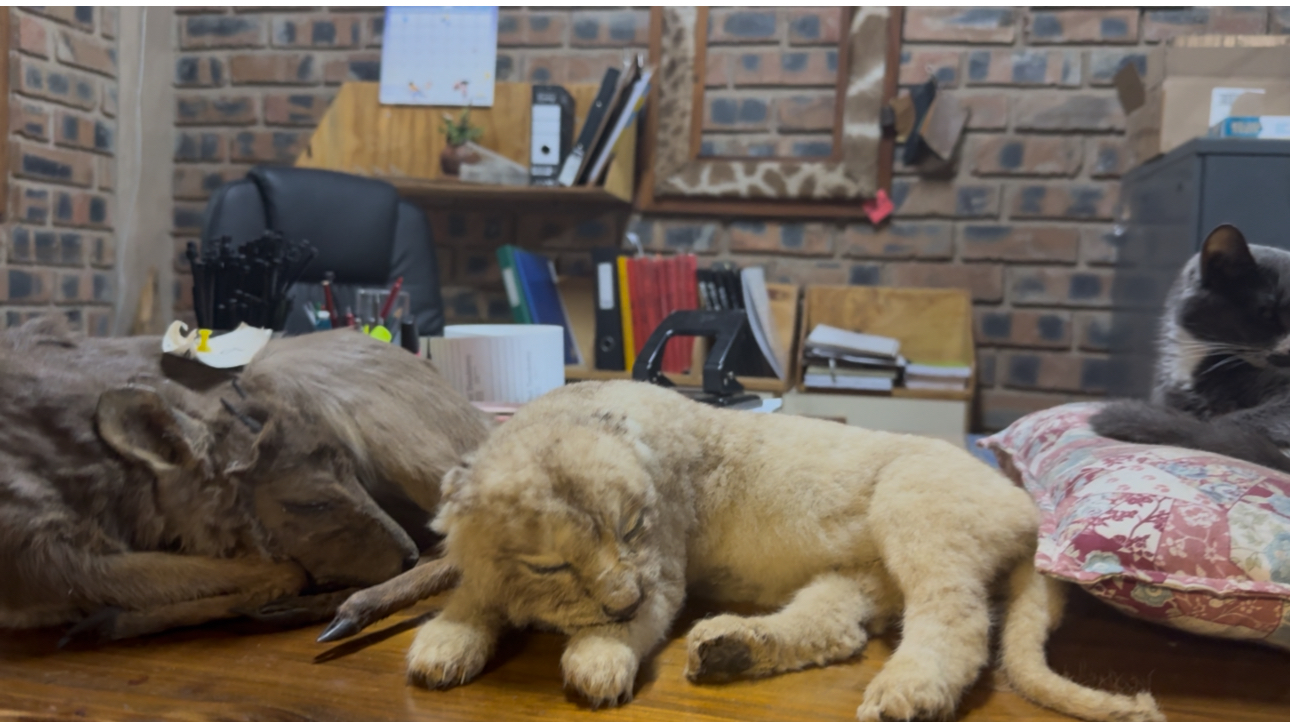
“We mount animals that have died naturally or were hunted… we use everything, from the meat to the skins and curls. It’s a sustainable way of doing business, and everything has a monetary value.”
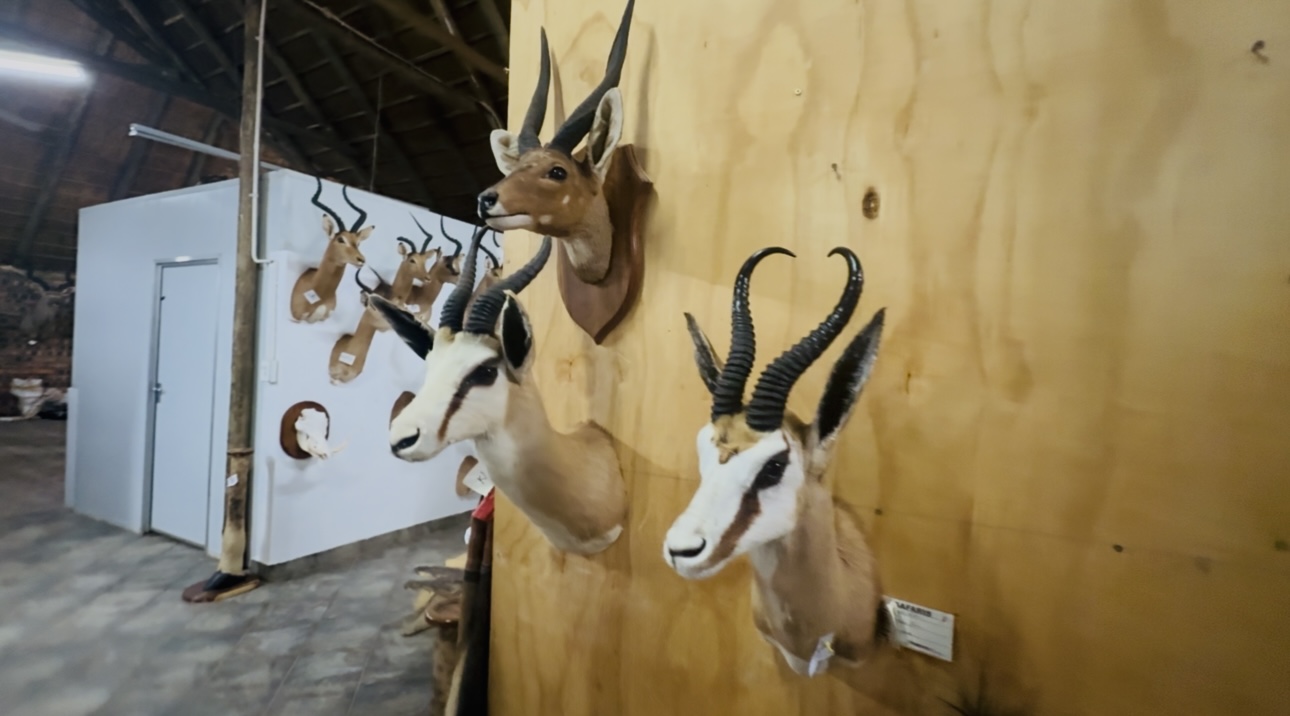

This, she says, is both business and passion — blending artistry, conservation, and commerce.
From workshops to global markets — taxidermy meets commerce
According to membership details o South African Taxidermy & Tannery Association, Estelle Nel Taxidermy offers a wide range of services: from mounting mammals, birds, reptiles; tanning skins and capes; cleaning, mounting and articulating skulls, bones, horns, tusks; to producing novelty leather items, polished horn décor, engraved bones, hoof lamps — even gunbags and furniture. They offer full export packing and crating services, and help clients ship internationally.
What this means is that skins, hides and trophies — once the culmination of a hunt — become far more than personal souvenirs. They become export commodities, contributing to livelihoods of artisans, packers, shippers, and everyone in between.
Yet, as Pieter Swart President of South African Taxidermy & Tannery Association (SATTA)/chairman of SUCO-SA) told us, that path to global markets is not without obstacles.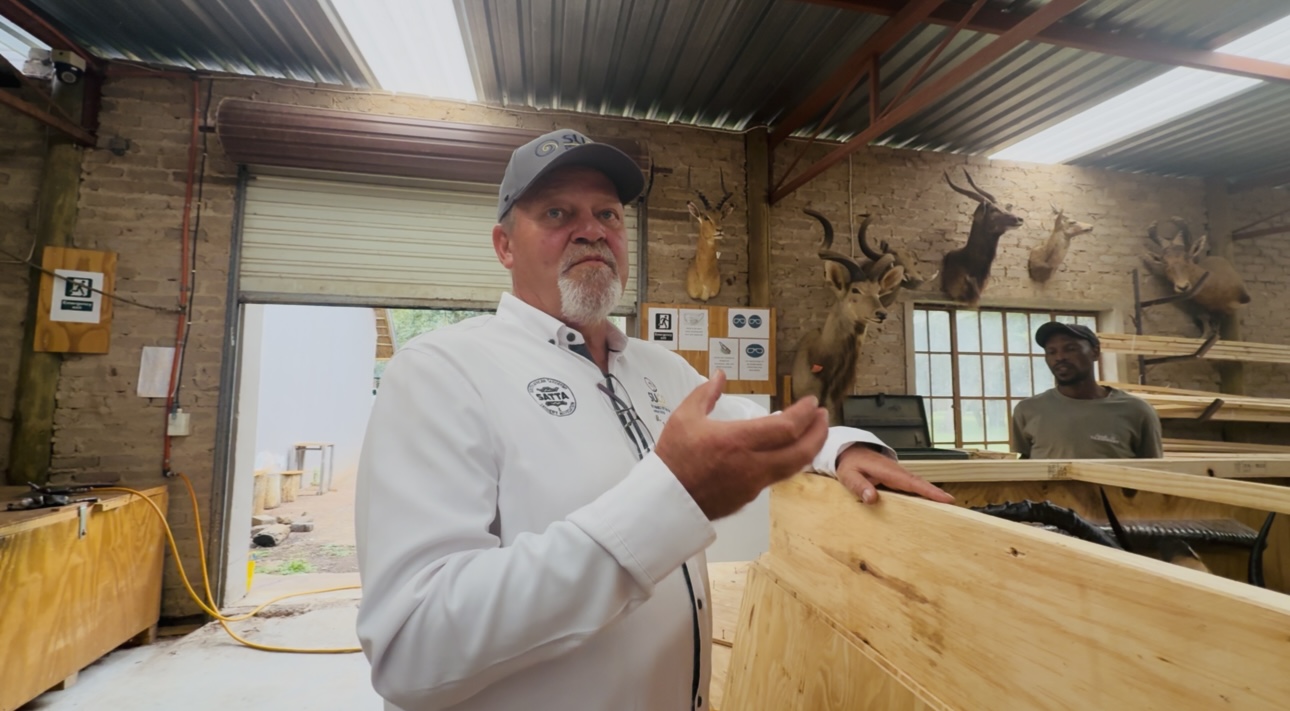
“Certain airlines allow the shipping of these trophies. I think it’s about four airlines that you can ship them overseas, but the rest refuse to take their hunting trophies to destinations. As well as the sea shipments — there’s only one ship going to America every three months. The rest of the shipping lines refuse to take hunting trophies.”
He lamented the difficulty in logistics. And yet, he sees themselves as part of a broader — and misunderstood — effort. “This anti-animal works movement created the idea that hunting is killing the animals and destroying them to extinction — but that is actually quite the opposite,” he said. “More and more, the guys are farming the animals; that is creating a better future for the animals.”
In other words: regulated, sustainable use — of every part of the animal — can coexist with conservation, economic empowerment, and community upliftment.
Game meat: from farm to fork
Next door to the taxidermy showroom, we toured a modest but hygienic meat-processing Camo Meat facility, run by people like Ina Hechter. They explained that their business started small — in 2012 as a private processing butcher for animals from farms. Around 2017 they expanded into wholesale for local markets. Export remains limited, but local demand is growing.

Their meats include species typical of the South African game-meat industry: kudu, impala, springbok, wildebeest, zebra and others. What began as a niche — somewhat stigmatised — trade is slowly gaining acceptance. Some supermarkets and lodges are carrying game meat; more restaurants are offering “veld flavour.”
Ina told me that in times of drought — when traditional livestock farming may suffer — game-meat businesses often see increased activity. Farms with overstocked wildlife or animals unable to survive drought may harvest and sell meat, skins and other resources. In this way, what might have been a loss can become income, conservation, and food security.
“Our parks are so small that they can’t sustain all the animals that are there,” Ina said. “Especially in drought years … when it’s not raining a lot you will see they die and then they sell the animals.”M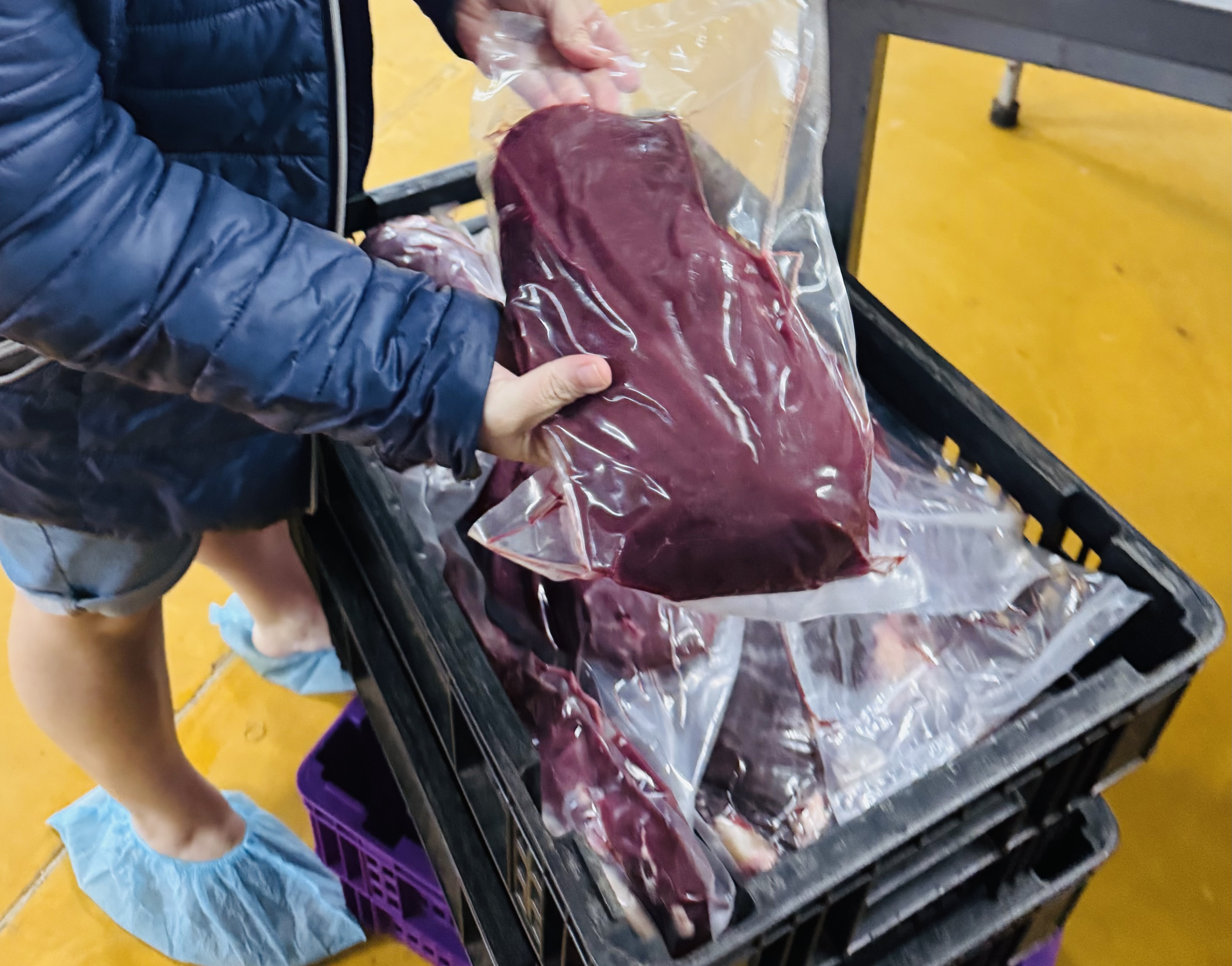
She sees game meat not only as a business, but as part of a broader sustainable economy — offering healthy, lean protein to consumers, easing pressure on overburdened habitats, and circulating value in rural and peri-urban communities.
More than meat and trophies — a conservation-economy model
What struck me during the tour was how holistic the operation is. It isn’t just about hunters bringing back trophies. It’s about using every bit of what exists: meat, skins, hides, horns, bones — even skulls, and decorative by-products. From full-body mounts to polished horn décor, from retail game-meat packages to furniture made from hoofs: this is a full-value chain.
Companies like Estelle Nel Taxidermy are members of formal trade associations and provide professional services — tanning, mounting, packing, export documentation — and in doing so, they help formalize trade in wildlife products.
Meanwhile, the game meat industry — though historically informal — is slowly growing more regulated. According to a recent national biodiversity-economy strategy, game-meat production supports economic growth, food security, and employment. The most commonly produced and consumed species: impala, kudu, wildebeest, springbok.
In other words: when properly managed, this sector has the potential to transform perceptions of wildlife — from being simply “wild animals” to resources that can feed, employ and uplift entire communities.
Challenges — logistics, stigma, regulation
But it’s not all smooth. As Pieter Swart highlighted, export logistics remain a bottleneck: only a few airlines transport trophies; shipping lines are often reluctant; sea freight to markets like the United States may come only every few months. This makes it harder for the industry to scale globally.
Domestically, the market for game meat and wildlife products still battles cultural and regulatory stigma. Many people still frown at game meat; supermarkets and restaurants are only slowly integrating it.
Regulation is another issue: for the industry to be sustainable, wildlife needs to be farmed or managed responsibly, harvesting must follow quotas, and processing must meet health and safety standards. When abattoirs, tanneries, and exporting agents comply with regulation, this gives the industry legitimacy — but it also requires oversight, capacity, and buy-in from all stakeholders.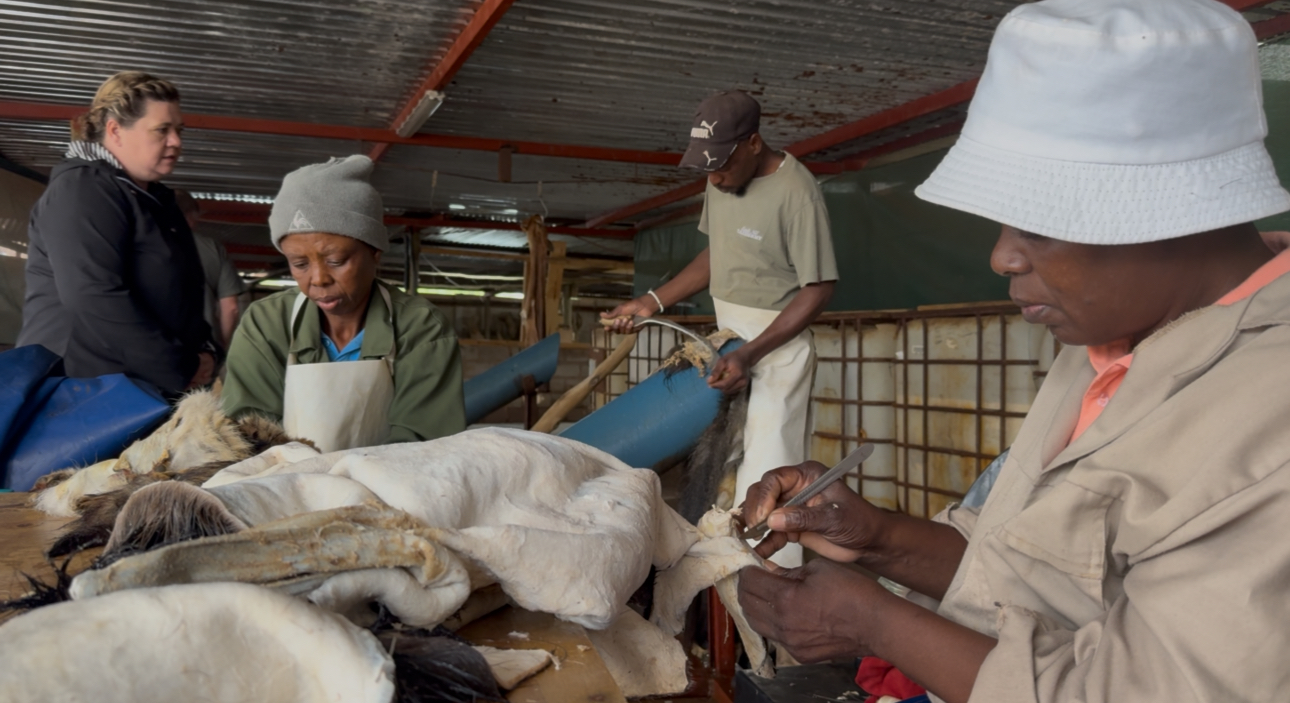
A snapshot
Our visit painted a picture of a wildlife economy that’s evolving: where skilled artisans turn skins, horns, skulls into enduring art; where processors supply game meat to homes, restaurants and hotels; where farms, outfitters, taxidermists, meat processors, exporters, and even children (learning from mounted displays) all form part of an ecosystem.
It’s a world that challenges simplistic ideas of wildlife as either “pristine wilderness” or “endangered species.” Instead, it shows how — if managed with respect, regulation, and purpose — natural resources can sustain livelihoods, build economies, and forge a bridge between conservation and commerce.
For many of those involved — from Melanie Viljoen to Ina Hechter and Pieter Swart — it’s not just business. It’s home. It’s art. It’s the future.

 Slider3 years ago
Slider3 years ago
 National4 years ago
National4 years ago
 Tourism and Environment4 years ago
Tourism and Environment4 years ago
 Opinion4 years ago
Opinion4 years ago
 Special reports4 years ago
Special reports4 years ago
 National4 years ago
National4 years ago
 National3 years ago
National3 years ago
 National3 years ago
National3 years ago










