BY BUSANI BAFANA
When driving at night in Zimbabwe, watch out for a pair of eyes on the road and slow down.
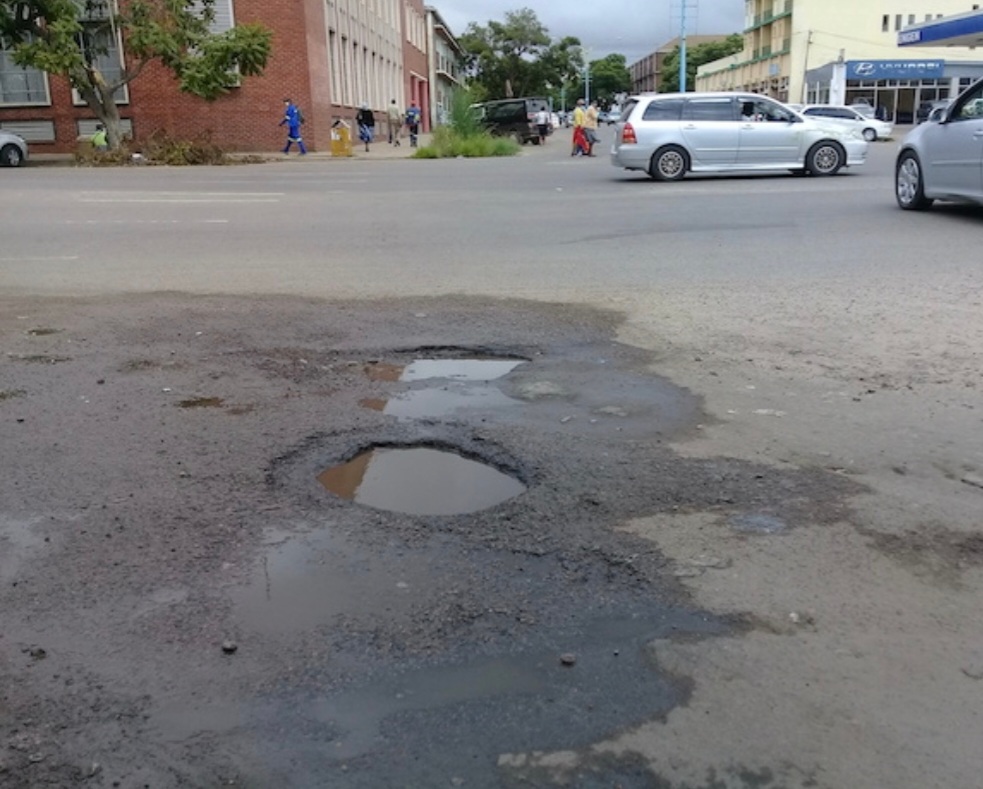
You may hit a giraffe inside a pothole. So goes an often-told joke.
It may be an unflattering hyperbole about the quality and safety of Zimbabwe’s roads, but it is not far from reality.
Zimbabwe’s roads are not famous for their aesthetics, nor quality and least of all, their safety.
Last year more than 2000 people died on the country’s roads, and scores of others were injured.
About five people on average die every day in road crashes in Zimbabwe, according to a review report on the country’s road safety launched in January 2022.
However, the World Health Organisation reckons the realistic figure is three times more.
The discrepancy may result from the government counting only deaths on the scene of the crash.
In contrast, global practice counts deaths within 30 days after the crash, says Lee Randall, an occupational therapist and road safety researcher, explaining that many countries in Africa have poor statistical systems and do not generate timely and accurate crash data.
Zimbabwe’s road safety review, conducted by the United Nations Economic Commission for Africa (UNECA) in partnership with the UN secretary-general’s special envoy for road safety, the United Nations Economic Commission for Europe (UNECE) and the government, sought to reduce road crash deaths and injuries in the country.
High road crashes, a toll on the economy
Road traffic crash deaths in Zimbabwe rose by 34 percent between 2011 and 2019, while fatalities rose from 1 836 deaths in 2016 to an average of 2 000 deaths per year between 2017 and 2019, the report found. Bus drivers and passengers accounted for 50 percent of the fatalities.
Road crashes, blamed mainly on a combination of human error, poor road infrastructure and defective vehicles, take a toll on lives and the economy in terms of health care costs.
Launching the review, United Nations Economic Commission for Africa (ECA) Executive Secretary Vera Songwe noted that the cost of road crashes is heavy on the African economies, especially as they try to rebuild amidst the effects of the Covid-19 pandemic.
“Anything that takes away from Africa’s GDP growth becomes important because we need every bit of it to move forward better,” said Songwe.
“The request by the Zimbabwe authority to review their transport and safety is encouraging given the dire road safety situation in the country but also the economic context that is very difficult.”
Research in 2018 by the Traffic Safety Council of Zimbabwe indicates that the country experiences an average of 40 000 road traffic crashes which cost about US$406 million annually, and these account for an estimated 3 percent of Zimbabwe’s GDP at $14 billion.
“Zimbabwe is the only one of the Sadc countries that have called for this kind of road review and good for the government for doing it because it is a big step towards rectifying the situation of road crashes,” Randall told IPS.
“It is a wake-up call to see these grim realities of road crashes for countries especially low- and middle-income countries where crashes consume a huge proportion of GDP that could instead be used for development and alleviating poverty.”
Even the Global Economy’s Survey rates Zimbabwe’s roads poorly with a score of 2.8 in 2019 compared to the world average for quality of roads based in 141 countries at 4.07 points.
After Cameroon, Ethiopia and Uganda, Zimbabwe is the fourth African country to launch a road safety performance review report that takes stock of progress in implementing the first United Nations Decade of Action for Road Safety 2011–2020.
The Second Decade of Action for Road Safety targets to reduce road traffic death and injuries by at least 50 percent by 2030.
Randall, who has researched widely on the bioethics of road safety, believes that road crashes should not be happening in the first place because most are avoidable and could be minimised with proper attention to the overall road traffic system.
Enforcement of road rules is critically important, and robust, well-resourced enforcement systems are important, but Randall said you cannot have traffic cops on every kilometre of every road every hour of every day.
“We have to appeal to our inner traffic cop, which is our moral sense that rests on a good level of insights into what the crash risks are and into human behaviour and literal training on what the laws are in a particular country.
“We need to drill road safety concepts into people at an early enough age to influence their behaviour in the road traffic system over their lifetimes,” said Randall. He is a founder of the Road Ethics Project, a non-profit company that engages people in ethical conversations and recognises individuals who have effectively contributed to reducing road crashes, injuries and deaths.
Second-hand cars and poor safety checks
Songwe also noted an increase in the importation of second-hand vehicles in Zimbabwe and other African countries, urging for a reduction in the importation of cars that are not up to standard that cost lives and are detrimental to economic development.
“As a continent, we need to take off importation of vehicles that are not up to standard that end up costing lives and are detrimental to economic development,” Songwe said.
Zimbabwe imports vehicles worth over $340 million annually, according to figures from the national data agency, Zimstat.
In 2021 Zimbabwe, through a Statutory Instrument, banned the importation of second-hand vehicles ten years and older.
But that has not stopped the grey imports, which ordinary Zimbabweans can afford to drive, a sharp contrast to the top-end luxury vehicles government splurges on.
High deaths, low investment in road safety awareness
The review made several recommendations for Zimbabwe to improve road safety, noting that the country had the worst road crash mortality rates among its neighbours.
Jean Todt, United Nations secretary-general’s special envoy for road safety, said Zimbabwe could reverse its high crash deaths rate if it implemented the review report’s recommendations.
Todt said 90 percent of people and goods in Africa are moved by road and that transport and mobility can only be sustainable if it is safe.
Africa has the highest road fatality rates per 100 000 people. Globally 1.3 million people are killed every year from road crashes, and over 50 million are injured.
It was recommended that Zimbabwe establish a road Crash Database and improve its statistical indicators and disaggregated data while implementing a post-Crash Care Response and Coordination System.
Currently, Zimbabwe does not have a single national three-digit emergency call number to facilitate timely road crashes and response reporting.
The review report also recommended developing a 10-year national road safety strategy and action plan to improve road safety in Zimbabwe by 2030 and the establishment of a Road Safety Fund.
Speaking at the launch of the review report, Zimbabwe’s deputy minister of Health and Child Care, John Mangwiro, said the country was committed to road safety by implementing recommended actions, including opening a crash and emergency reporting institution.
Poor medical health systems had meant that many survivors of road crashes died when they reached hospitals owing to the lack of post-crash care.
The review had good news. Zimbabwe can accelerate road safety and reverse road crashes by investing in public education on road safety, implementing effective policies and improving the road system infrastructure.
On the road to better roads
Last year the government declared the country’s road network a state of disaster. It announced an allocation of $400 million to fund road rehabilitation and upgrading through the Emergency Roads Rehabilitation programme.
The Zimbabwe government recently announced an ambitious road development plan to rehabilitate the country’s road network, which covers more than 78 000 km.
Some of the roads are more than 30 years old. – IPS


 Slider3 years ago
Slider3 years ago
 National4 years ago
National4 years ago
 Tourism and Environment4 years ago
Tourism and Environment4 years ago
 Opinion4 years ago
Opinion4 years ago
 Special reports4 years ago
Special reports4 years ago
 National4 years ago
National4 years ago
 National3 years ago
National3 years ago
 National3 years ago
National3 years ago