BY LENIN NDEBELE
With just six months before the time is up for those in South Africa living under the Zimbabwe Exemption Permit (ZEP), there are mixed feelings among Zimbabweans, with some wishing for a further extension, while others contemplate going abroad.
The government announced that it would terminate the ZEP on 30 June 2023, a decision that will affect about 180 000 Zimbabweans residing in South Africa.
As early as October, the Zimbabwean government announced that it was prepared for its nationals who were coming home to start a new life and would assist them with transport and other logistics.
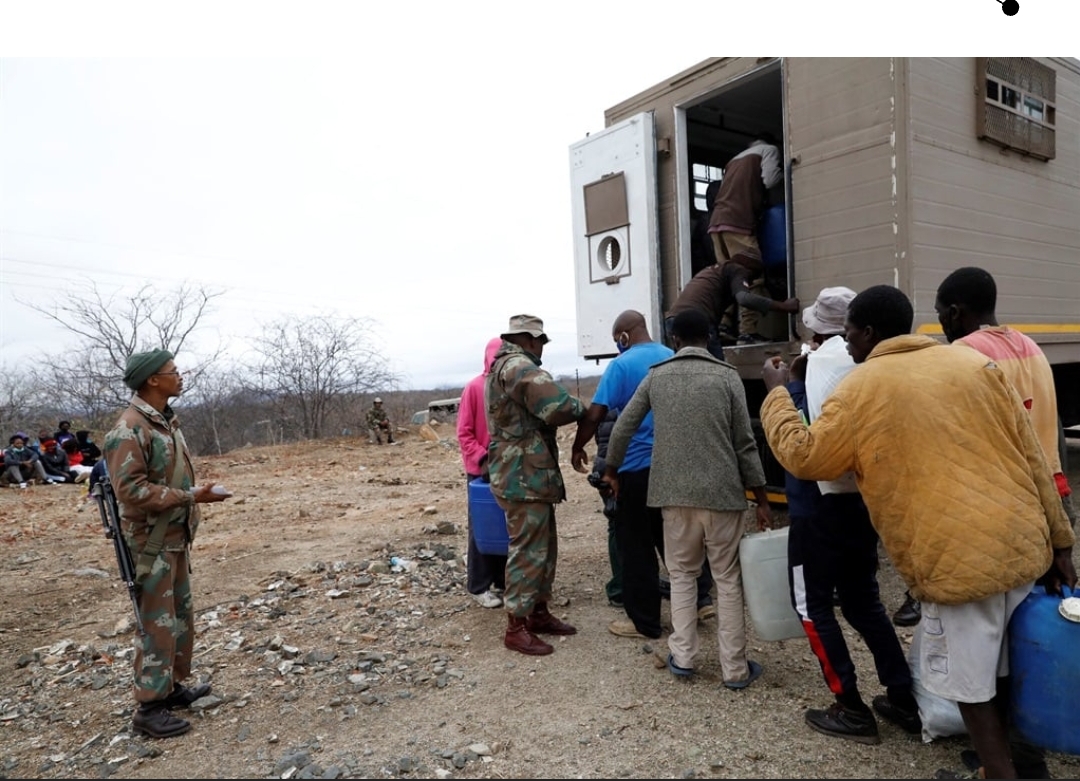
While there has been no sign of it backing its words with action, there has been an influx of travellers from South Africa into Zimbabwe.
Between 5-10 December, 62 770 people entered Zimbabwe through the Beitbridge border.
The head of immigration at the border, Cannie Magaya, said although they had no figures yet, on the days leading up to Christmas, there had been an increase in traffic.
She said it could stay like that until early January when people start returning to South Africa.
Brian Moyo, a Zimbabwean working as a teacher in SA, didn’t apply for the special skills visa because he felt it was a waste of time.
While he is going back home in early January, he has set his sights on jobs in China.
He said: “I teach English and that’s not a special skill. I stood a chance as a science or mathematics teacher, as such, applying for other visas was a waste of time for me.
Moyo, before migrating to South Africa, taught at some private schools back home.
He feels his experience there could help him in China.
“There is a demand for teachers in early education in China, and English language is one of the subjects with vacancies. So I am applying for those jobs, and one advantage I have is understanding children’s psychomotor skills and capacity to learn,” he said.
An online search by News24 discovered that salaries for teaching jobs in China range from R70 000 to R120 000, depending on the type of school and level of experience.
In comparison to teaching jobs in southern Africa, Chinese teaching jobs pay way better.
Another opportunity will come into effect in March when the United Kingdom opens up for teachers from South Africa, Ghana, Zimbabwe and Nigeria.
But Moyo said he had not considered that option yet, since it was yet to be offered.
Working in South Africa has also become very difficult for those spending their money in Zimbabwe because of the rand’s volatility against the US dollar, the preferred currency of trade.
During the festive season, R100 is the equivalent of $5.80, but most shops or businesses only value it at $5.
“It’s robbery,” said Steven Tshuma, another Zimbabwean based in South Africa.
He added: “They don’t respect this (rand) currency. One is better off coming from Europe or elsewhere.”
‘I hope my boss comes up with a plan’
With the impending ZEP expiry, he is setting his eyes on the UK, Canada or Australia.
“I am starting a nurse aid course with the Red Cross (in SA) early next year. When done, I will apply for jobs abroad. Many have done it. It works,” he said.
Tshuma works at a restaurant and has come face to face with members of Operation Dudula – a vigilante group that intimidates migrants.
He is worried that, a few months before permits expire, xenophobic attacks could resurface, and that by then they would be extreme, because they would be targeting people who had been outlawed by the government but chose to stay on illegally.
He said: “What excuse would I have to be in SA? They could burn us alive, because first and foremost we would be illegal immigrants and going to report criminal conduct at a police station would be getting yourself arrested.
By the end of October, fewer than 10% of ZEP holders had applied for the available mainstream visas.
An estimated 180 000 ZEP holders will be affected by the 30 June 2023 deadline set by the government.
Shiela Ncube, a domestic worker in Johannesburg, has no plans of leaving the country.
She hopes her boss will find a way around the system to keep her in SA-News24

 Slider3 years ago
Slider3 years ago
 National4 years ago
National4 years ago
 Tourism and Environment4 years ago
Tourism and Environment4 years ago
 Special reports4 years ago
Special reports4 years ago
 Opinion4 years ago
Opinion4 years ago
 National4 years ago
National4 years ago
 National3 years ago
National3 years ago
 National3 years ago
National3 years ago