BY JEFFREY MOYO
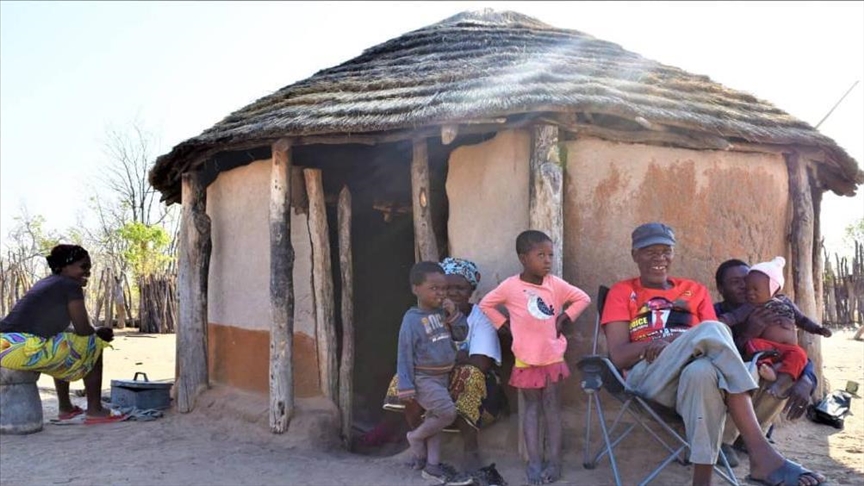
Nyaliwe Mendisi has never known the door of a classroom.
None of her 12 children went to school, and now the 81-year-old’s grandchildren and great-grandchildren have had no basic education either.
Mendisi belongs to the San community, together with her unschooled grandchildren and great-grandchildren.
Now stung with poverty, the only jobs her children and grandchildren have known are domestic employment in the villages of Tsholotsho, in Matabeleland North Province.
Most of her grandsons and granddaughters are employed as cattle herders or tend other villagers’ fields.
“My whole generation in my family has never been to school. We have nothing of value that we own to enable children to attend school. We have no goats nor cattle that we can sell to raise school fees,” Mendisi told Anadolu Agency.
Also known as the Bushmen or Basarwa, the San, which is Mendisi’s tribe, were the first Bantu people to dwell in present-day Zimbabwe.
Mired in poverty, many San people like Mendisi and her descendants, populate remote areas of this southern African nation, with others facing similar situations in other countries like Angola, Botswana, Namibia, South Africa, and Zambia.
In Zimbabwe, some of the apparently forgotten tribe lives in Plumtree in Matabeleland South Province.
Now, as the World commemorates International Day of the World’s Indigenous People annually on Aug. 9 by the UN, Zimbabwe’s Khoisans, like Mendisi, have nothing to celebrate amid mounting penury.
“Food is even hard to get because this region always gets very low rainfall. We have no cattle nor donkeys that we can use for our farming,” she said.
But what worries many like Mendisi and her family is the lack of national identity cards, which means together with her descendants, they have contended with statelessness.
“Having no IDs or birth certificates has meant none of us gets the opportunity to go to school or even dream of having a bank account,” Mlungisi Mendisi (23), a grandson on the matriarch, told Anadolu Agency.
Even decent shelter for the San tribe is something that they can only fathom in their imaginations, according to the younger Mendisi, who also said he has never had a bus ride or boarded a car.
With incessant droughts pounding Zimbabweans more often, the San have not been spared but getting food donations from the government has remained a mountain task for many like Mlungisi without identity documents.
“No ID no food from the government and some of us just have to starve. It has never been easy for many of us to get identity documents like birth certificates and national identity cards,” he said.
Davy Ndlovu, programmes manager for Tsoro-O-Tso San, a development trust that fosters the rights of the San tribe, said the minority tribe has for centuries faced broad injustices, leading to poverty situations for generations.
“Since the San’s removal from their ancestral land to pave way for the establishment of the Hwange National Park in 1928, their lives as hunter-gatherers were disrupted.
“Today, they live lives of poverty in the outer edges of society and are struggling to adapt to a sedentary lifestyle,” Ndlovu told Anadolu Agency.
To Ndlovu, like many minority groups in Zimbabwe, the Khoisan people are not strangers to segregation.
“Many minorities in Zimbabwe suffer discrimination and the situation is even worse for the San,” he said.
According to Tsoro-O-Tso San, there are approximately 2,500 San people living in Zimbabwe.
Even as Ndlovu and his organization have tried to help many Khoisan to enroll in school, families like Mendisi’s have had no chance.
But organizations like Tsoro-O-Tso San headed by Ndlovu, have tried to extricate many of Khoisan descendants from poverty.
“When we started our project in 2010, few of the San children finished primary education. After numerous awareness campaigns on the importance of education, quite a number has gone up to form four, with others even finishing form six of their secondary education,” said Ndlovu.
To Ndlovu, even as the Khoisan tribe remains downtrodden and apparently forgotten by authorities, there is something to smile about.
“For the first time ever, we have three Khoisan descendants attending university.
There is however little support from the government and this has left many San children uneducated,” said Ndlovu.
Health-wise, Ndlovu said the Khoisan are faced with trouble as health facilities are still few and people are forced to travel long distances to seek medical attention.
Ndlovu said with many San people still stateless here, several, like Christopher Dube of Garia village in Tsholotsho, have recently battled to bury an undocumented relative who died in neighbouring South Africa, also without personal documents.
According to Ndlovu, the deceased is still unburied in South Africa due to a lack of proper documentation. – Anadolu Agency.

 Slider3 years ago
Slider3 years ago
 National4 years ago
National4 years ago
 Tourism and Environment4 years ago
Tourism and Environment4 years ago
 Special reports4 years ago
Special reports4 years ago
 Opinion4 years ago
Opinion4 years ago
 National4 years ago
National4 years ago
 National3 years ago
National3 years ago
 National3 years ago
National3 years ago