BY NOKUTHABA DLAMINI
Livingstone, Zambia — In Maloni township, the sound of glass snapping cleanly against a cutter echoes through the yard of a modest home. What was once a discarded beer bottle now sits neatly trimmed, smoothed into a drinking glass. For a group of young men long dismissed as “junkies,” this simple act has become the beginning of a second chance.
At the centre of this transformation is Songiso Mukena, a conservationist, tourism practitioner and founder of the Responsible Earth Keepers Foundation (REK). Through conservation work, recycling, football and mentorship, Mukena is quietly rewriting the futures of boys once written off by their own communities.
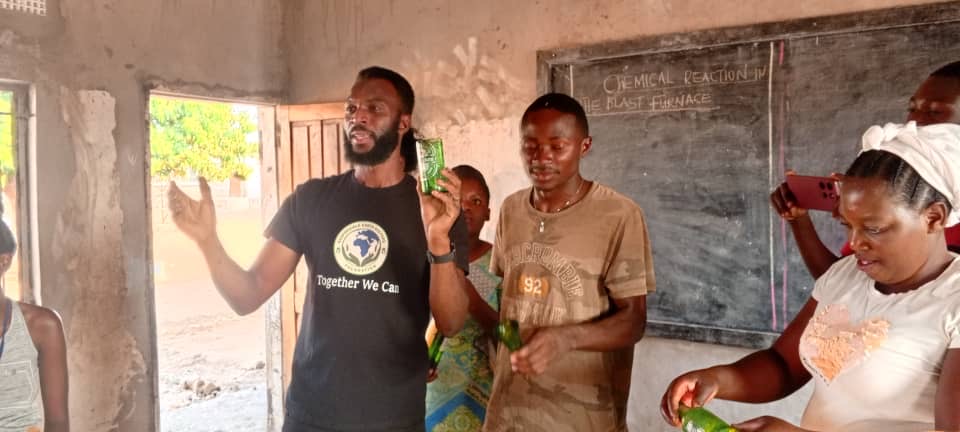

“My name is Songiso Mukena from Livingstone, Zambia,” he says. “I am the founder of Responsible Earth Keepers Foundation – a non-profit making organisation.”
A journey rooted in hospitality and conservation
Mukena’s passion for conservation grew out of more than 15 years working in Zambia’s hospitality industry. While employed at Jolly Boys Backpackers in Livingstone, he was involved in a programme focused on responsible tourism and waste management.
“For me, it was just work,” he explains. “It was all about waste separation, finding a better place where to take or whom to give. We were doing worm farming and also just learning how to manage waste.”
That experience sparked a deeper interest. “I think it’s one of the places I worked that really opened my mind,” he says.
In 2016, a visit to a recycling organisation became a defining moment.
“I was amazed with what I saw,” Mukena recalls. “They were giving life back to bottles that were discarded out there or thrown out. They would cut them, make candle holders, lanterns and drinking glasses.”
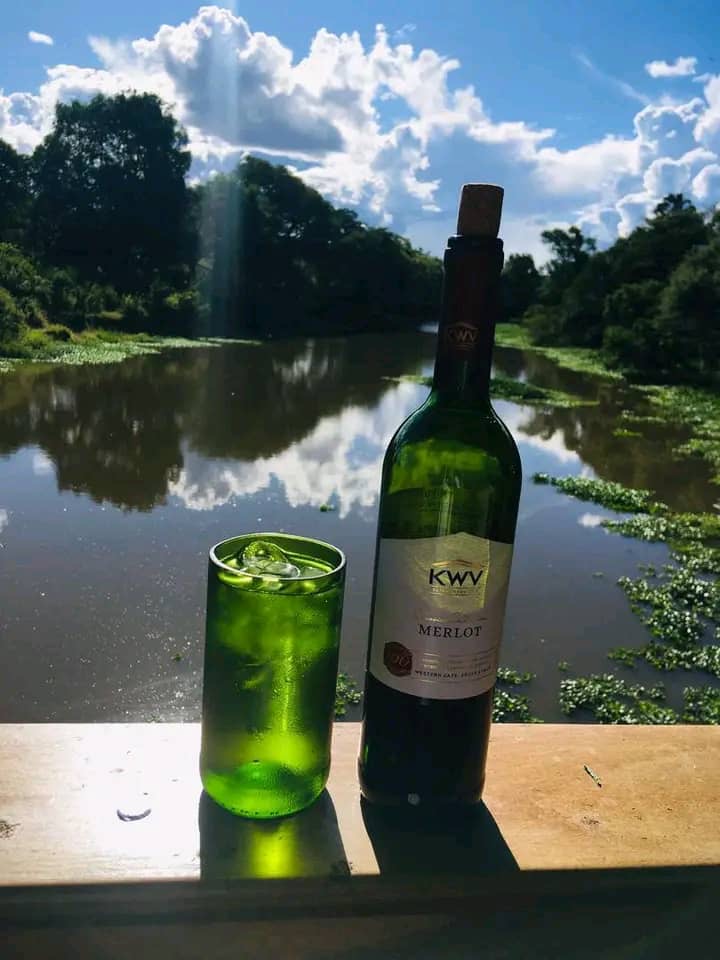

Although he wasn’t taught the technique, the idea stayed with him. “I started doing research on how to cut a bottle and make a drinking glass,” he says. “It wasn’t easy.”
A breakthrough came when former employers, Mr and Mrs Sikaneta of Munga Eco-Lodge, donated a glass cutter.
“I started practicing and practicing,” Mukena says. “The whole of 2017 I was practicing. In 2018, I started taking bottles to my house and cutting them.”
Soon, people began buying the glasses.
“For me, my mind shifted,” he says. “I thought, I think this can be a big idea on recycling.”
COVID-19 and a move into the community
The COVID-19 pandemic forced Mukena out of employment as tourism ground to a halt. He moved from Linda township to his own plot in Maloni, an area facing deep social challenges.
“It’s a remote area,” he explains. “It’s one of the places where you find early pregnancies, boys failing exams and turning into what today are called junkies.”
Many of these boys had gone through traditional initiation ceremonies, after which they were often stigmatised.
“When they come back, the community views them in a different way,” Mukena says. “Once you go there and come back, you are not taken as a normal boy child.”
Instead of distancing himself, Mukena opened his space to them.
“I started teaching those boys how to cut bottles, making drinking glasses,” he says. “We started with about ten boys.”
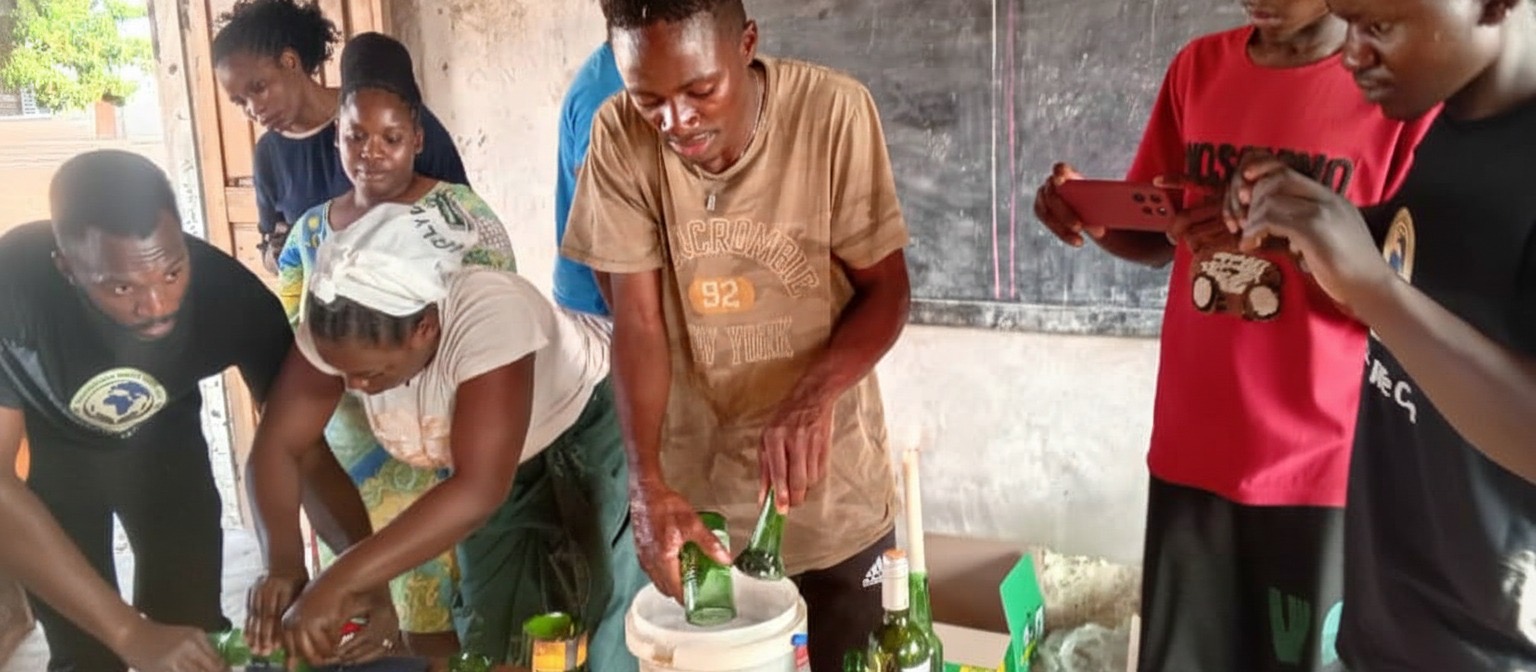

The glasses were sold, and the money shared according to need.
“If one lacked shoes, we would sponsor that,” Mukena explains. “If another boy wanted to go back to school and lacked books, we helped.”
Healing beyond skills
The transformation was not just physical or financial. Mukena’s wife, Yvonne, a psychosocial counsellor, joined the initiative.
“She started talking to the boys,” he says. “Trying to get their minds shifted.”
Their home became a safe space.
“Our home became a home of many,” Mukena says. “Some kids would come just to play.”
Recycling soon funded broader social causes.
“We said, how about we sell these glasses back into the charity to help make it self-sustainable? Mukena explains. “Waste management became a starting point for other projects.”
Football as a tool for dignity
Football emerged naturally from the boys themselves.
“They were already playing – and with real talent,” Mukena says. “One day they came and said, ‘Father, we want to play City Stars and we’ll win!”’ City Stars is a professional team.
Recognising their talent and passion, the boys asked for support.
“They said, if possible, can you organise football kits for us?” he recalls.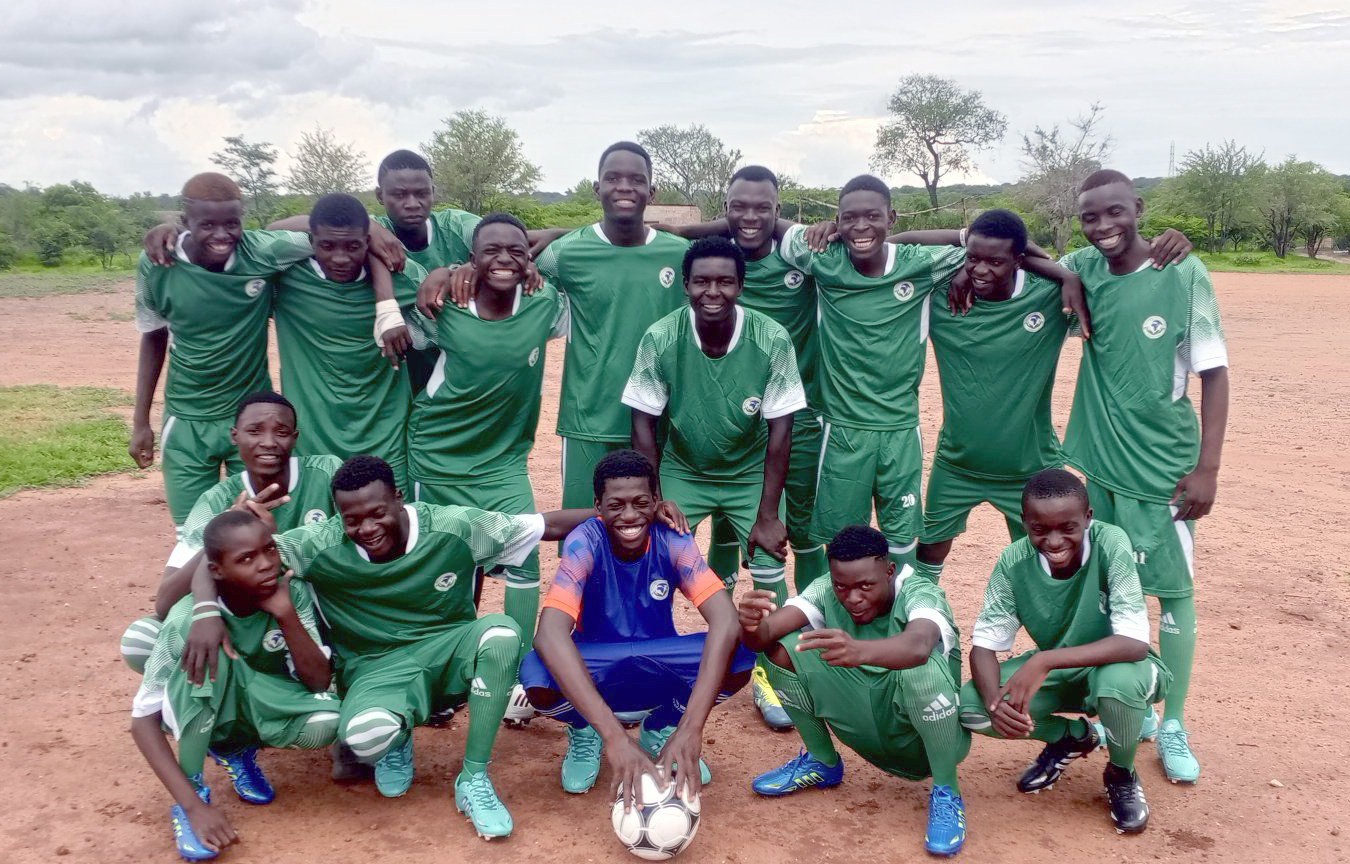
A local church donated land for a pitch, and REK FC was formed. Recycling income helped support the charity’s activities, linking conservation directly to sport.
Football also brought structure, discipline and confidence.
“We don’t just concentrate on soccer,” he says. “We also give motivational talks, encouragements, testimonies and Bible readings. At the end of the day, it’s a mind change that we are looking for.”
Support from abroad, built on trust and friendship
Among those drawn to support Mukena’s work were two tourists from the UK, Simon Greene and Audrey Furnell. Simon explains why grassroots initiatives resonate with donors today:
“In return for a relatively modest donation anyone can make a tangible difference. Supporters like us can see a direct return on what we give which is incredibly rewarding.”
Simon says this is exactly the kind of work they want to promote.
“We’ve learnt a huge amount from Song and Yvonne and were struck by their kindness and impressed by their drive to do more for his community,” Simon says.
Their family’s support began with a classroom project in Linda, expanded to monthly assistance for school needs, and later funded a borehole near Kazungula.
When introduced to the boys of Maloni, Audrey says:
“We saw their passion for football and it was clear they deserved the chance to be their best on the field – but without proper kit that could never happen.”
Soon afterwards, Simon recalls:
“Songiso lost no time, organised all the kit and immediately arranged a match on Christmas Eve with REK FC playing against a professional team. We were thrilled.”
Rewriting the story of the boy child
Mukena believes the project addresses a wider national issue.
“There was a campaign for educating the girl child,” he says. “That campaign was done very thoroughly. But the boy child was left behind.”
He believes that neglect has contributed to rising numbers of boys labelled as criminals and drug users.
“When a boy’s mind is changed,” Mukena says, “it’s an achievement for the organisation, the community and the country.”
Today, REK works with approximately 100 boys aged between 15 and 22, with about 25 actively involved in recycling and football.
The long-term goal is to establish a recycling and skills training centre employing youth from the community.
“We want a better community,” Mukena says.
Small acts, lasting change
In Maloni, discarded bottles are no longer just waste. They are tools of transformation — funding education, restoring dignity and giving young men a reason to believe in themselves.
For Mukena, success is simple.
“One day we hope a boy will be picked to play for a professional team,” he says, “that will be an incredible achievement for him — and for us.”
And for Simon and Audrey:
“We feel blessed to have Songiso in our lives. Being able to see REK make valuable improvements like these is very rewarding. We’d like more people in the wider donor community to act as we have – together we can make a difference.”

 Slider3 years ago
Slider3 years ago
 National4 years ago
National4 years ago
 Tourism and Environment4 years ago
Tourism and Environment4 years ago
 Special reports4 years ago
Special reports4 years ago
 Opinion4 years ago
Opinion4 years ago
 National4 years ago
National4 years ago
 National3 years ago
National3 years ago
 National3 years ago
National3 years ago















 Key proposals Zimbabwe taking to CITES CoP20
Key proposals Zimbabwe taking to CITES CoP20