BY STAFF REPORTER
Doctors at government hospitals such as Bulawayo’s Mpilo Central Hospital are demanding bribes of up to US$700 to conduct surgeries on patients, the National Assembly has been told.
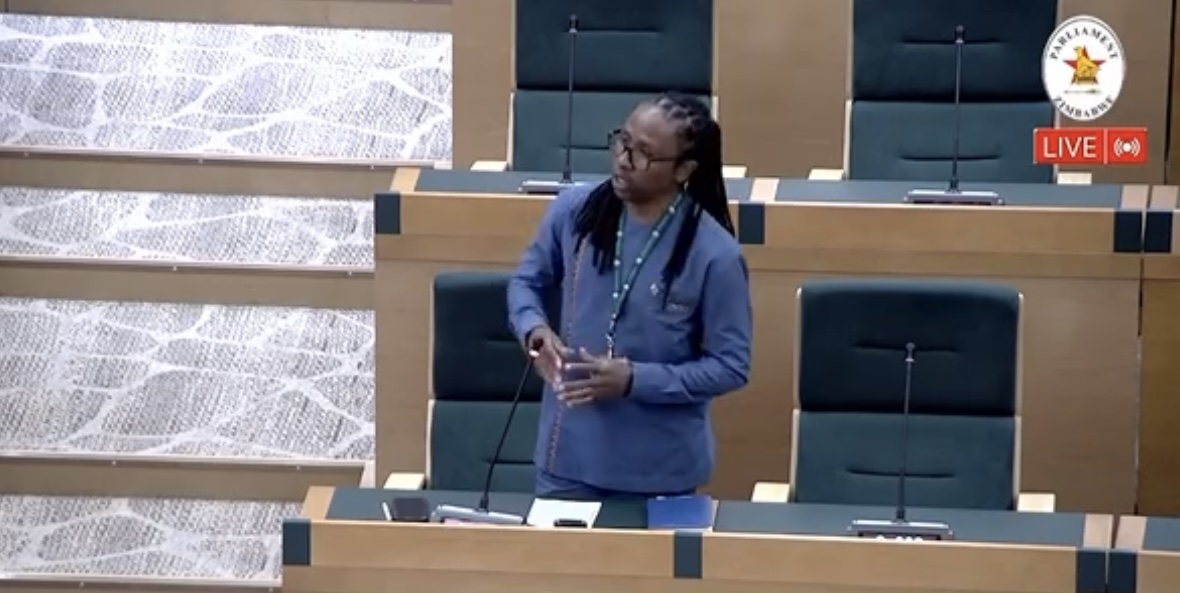
Makokoba MP James Sithole made the claims while raising a matter of national interest in Parliament on Thursday.
He said the developments were a sign of decay in the delivery systems at central hospitals.
“I will give an example of what is happening at Mpilo Central Hospital,” Sithole said.
“I am referring to corrupt activities, which are unnecessarily exposing patients that are already suffering to more suffering and to premature death.
“There are patients that have been on the queue to go to theatre since December 31, 2021 and they have not been able to have the opportunity to go to theatre.
“The reason is that each time their allocated dates arrive to go to theatre, excuses are given.”
He added: “They are told that there are no doctors to attend to them; they are told that there are no necessary materials in the theatre; they are told that their temperature is too high for them to go to theatre.
“However, the truth is that it is because they would have not paid a bribe to doctors that range between (US)$300 to (US$) 700 or more.
“Surprisingly, doctors are able to carry out procedures using the same theatres on their private patients without paying anything to the hospital.”
The MP said the X-ray machine and the scanner are said to be broken down most of the times.
“So, if ever anyone is lucky at that time to be attended to, when they get to the other end where the doctor is looking at the X-ray picture, the patient is told the X-ray is not clear because the X-ray machine is faulty,” Sithole added.
“So they are referred to facilities outside or private operators where they have to do another X-ray.
“On the scanning machine, pregnant mothers who have to do a scan are told that there is no jelly but surprisingly, again, the officer operating the scan will be having their private jelly.
“They only attend to their private patients from their private practice, but who come and use the hospital scan with the jelly.”
“Anyone referred by Mpilo is told that there is no jelly, yet those coming from outside who will be their private patients will be attended to.”
The legislator said patients are also denied the opportunity to buy medication from the dispensary as they would be told that medicines are out of stock.
He said when patients pay directly to nurses in the wards, the medication suddenly becomes available.
“So, these are some of the examples that are happening at Mpilo Hospital,” Sithole added.
“Therefore, I would request that the Ministry of Health and Child Care carries out an investigation and bring a ministerial statement to this House.”
National Assembly speaker Jacob Mudenda said Sithole had raised “a fundamental and profound observation.”
Mudenda related an incident where one of his relatives’ son with a broken arm went for six months without being operated on at Harare’s Parirenyatwa Hospital until he intervened.
He said Vice President Constantino Chiwenga, who doubles as Health and Child Care minister, would be asked to table a ministerial statement in the National Assembly to explain what was being done to curb corruption in public hospitals.

 Slider3 years ago
Slider3 years ago
 National5 years ago
National5 years ago
 Tourism and Environment4 years ago
Tourism and Environment4 years ago
 Special reports4 years ago
Special reports4 years ago
 Opinion4 years ago
Opinion4 years ago
 National4 years ago
National4 years ago
 National3 years ago
National3 years ago
 National3 years ago
National3 years ago