BY FORTUNE MOYO
When Chumani Sibanda-Ncube was a little girl, she was told it was the woman’s job to cook, clean, collect firewood and lug water back from the borehole — in short, to keep the house running.
In the village of Ntabayengwe, seven kilometres from Victoria Falls, this rigid division of gender roles is slowly changing.
“I’ve never imagined myself cooking,” says Sibanda-Ncube’s husband, Lovemore Ncube, grinning.
In Ntabayengwe, home to just over 1,000 people and where Ncube has lived all his life, men build and maintain the thatched huts in which families live, put up residential boundaries and work as herders.
Residents considered the kitchen — and all the responsibilities that come with it, including collecting firewood — to be the woman’s domain.
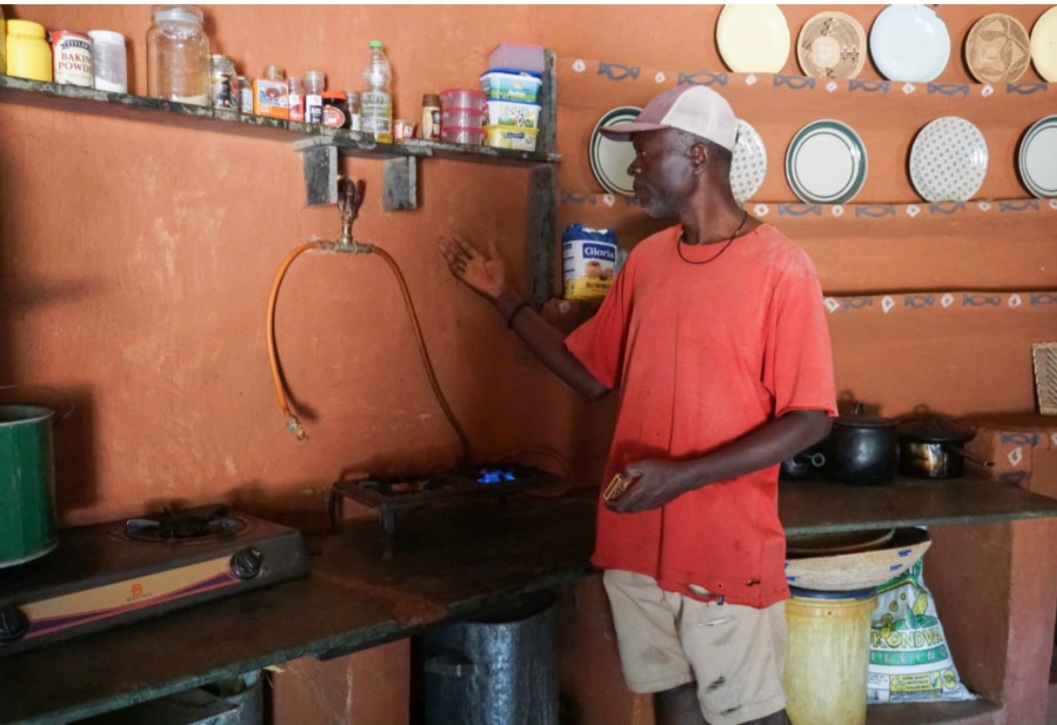
But with the installation in 2017 of a biogas digester, which uses cow dung to produce energy, Ncube no longer waits for his wife to return home from work.
He also prepares food for the children in the morning.
“When I get hungry, I can easily cook some food for myself — and sometimes for the family,” he says.
The contraption quietly driving this change — and simultaneously helping reduce deforestation in the area — is a dome-shaped device affixed to the ground just outside the house.
A pipe snakes in through the kitchen window, connecting the device to the family’s two-plate stove.
Biogas — the mixture of gases produced through the breakdown of organic matter such as agricultural and municipal waste — is a renewable energy source.
Over the past decade, a number of initiatives — some led by the government in partnership with international development organizations and others by local nongovernmental organisations such as the Jafuta Foundation — have introduced biogas digesters in rural Zimbabwe.
In the rural parts of Victoria Falls, biogas also is encouraged as a means of reducing deforestation near one of the country’s biggest tourist towns.
The biogas digester costs US$1,000, but Ncube says they didn’t have to pay for it.
The Jafuta Foundation, a local nonprofit that works with rural communities on issues of education and conservation, installed it free of charge.
When revved up the first time, the digester requires 400 kilogrammes of cow dung to begin working.
After that, however, dung from a single cow can keep it running for years.
Ncube says he shovels dung into the digester about once a month.
A family uses four trees’ worth of firewood a month on average, according to the Jafuta Foundation.
Those who use biogas have reported an 85 percent reduction in wood consumption, says Sipho Moyo, a project manager at the organisation.
Biogas has numerous uses.
Johannes Nyamayedenga, a spokesperson for the Rural Electrification Agency, a subsidiary of the Ministry of Energy and Power Development, says the agency has no data on how many rural households are currently electrified, but in 2012 the percentage stood at 13 percent.
“Biogas is one of the ways in which the country can use alternative sources of renewable energy because it uses easily accessible products such as organic matter,” he says.
In 2019, about 65 percent of rural households relied on firewood to run their homes — one reason for the country’s steep deforestation rate of about 262,000 hectares a year, says Violet Makoto, spokesperson for the Forestry Commission.
“The use of biogas, especially in rural areas in the country, has greatly reduced the amount of deforestation,” she says.
Makoto didn’t comment on deforestation rates in specific areas of the country.
Dry dung has long been used as a fuel in other parts of the world.
In Zimbabwe, prior to the introduction of biogas digesters, it was primarily used to layer the floors of huts.
This would keep homes warm in winter and cool in summer.
As of 2017, according to research by the Bindura University of Science Education, 711 digesters were installed across Zimbabwe, with 91 percent of them installed in households, where biogas is primarily used for cooking.
One reason for the slow rollout of the technology, the research notes, is the high cost of installation.
Nyamayedenga, the electrification agency spokesperson, didn’t provide more recent figures or comment on costs because the agency installs digesters only for institutions such as boarding schools and mission hospitals, not for individuals.
The agency has installed digesters at 11 institutions across Zimbabwe.
Households that wish to install digesters have to pay market price, says Nyamayedenga, adding that the government doesn’t regulate private providers.
As a result, most families making use of biogas digesters received them free of cost from nongovernmental organizations such as the Jafuta Foundation.
Of Ntabayengwe’s 132 households, 20 use biogas digesters.
“There was some resistance in the beginning as some villagers did not understand the concept,” Ncube says.
“Some would say they cannot eat food from cow dung. But they have since embraced the concept.”
As the smoke from wood fires has abated, respiratory problems in the village have also decreased, Ncube says
Biogas helps overall health, says Fungai Mvura, district medical officer, even if the decrease in firewood doesn’t have a noticeable impact on the number of respiratory illnesses.
“The biogas concept is good for the health of the community because it is considered clean energy compared to firewood, which produces smoke that is harmful.”
Women’s work, in particular, has become easier.
Sharon Tshabalala, who installed a biogas digester in 2020, says she no longer has to haul home firewood during the rainy season.
“It has become easier to prepare breakfast for the family in the morning, especially for my grandchildren who go to school,” she says.
Dorcas Mabhena, Ntabayengwe’s village head, agrees that the division of labor in some homes has shifted — but only a little.
“Gender roles are almost engraved in one from childhood,” she says. “It could take years for one to shift from that.”
Moyo points to another reason biogas digesters haven’t been fully embraced.
“It is difficult to totally convince the older generation to do away with making a fire in the home due to cultural belief,” he says.
In sub-Saharan African tradition, a hearth represents life.
Along with the kraal, where a family’s cattle are kept, and the silo, where harvested maize is stored, it’s one of the pillars of the homestead, says Ncube.
In addition to the biogas digester powering his kitchen, he has a small fire crackling in his home. – Global Press Journal


 Slider3 years ago
Slider3 years ago
 National4 years ago
National4 years ago
 Tourism and Environment4 years ago
Tourism and Environment4 years ago
 Opinion4 years ago
Opinion4 years ago
 Special reports4 years ago
Special reports4 years ago
 National4 years ago
National4 years ago
 National3 years ago
National3 years ago
 National3 years ago
National3 years ago