BY OWN CORRESPONDENT
Zimbabwe is set to get more than five million Covid-19 vaccines in the coming few weeks after the African Union (AU), African Vaccine Acquisition Trust (AVAT) and Unicef secured 400 million doses of the Johnson & Johnson vaccine.
The country last month approved the emergency use of Johnson & Johnson’s Covid-19 vaccine in addition to other registered vaccines from India, Russia and China, as government ramps up efforts to inoculate more than 10 million people Zimbabwe to get herd immunity.
Like many African countries, Zimbabwe is in the throes of a third wave of infections, after the country registered 112,435 cumulative cases and 3,676 deaths, while over 2.5 million had been vaccinated by Tuesday this week, according to official data.
Experts said the AU, Unicef and AVAT partnership, which seeks to ensure seamless procurement and delivery of vaccines to AU Member States, will help boost efforts to mitigate the impact of the pandemic as less than two percent of people on the continent are fully vaccinated so far.
“We are building a platform for deeper collaboration that will pave the way to a more robust African response to the pandemic and move the continent towards recovery, leveraging the opportunities to strengthen health systems and support the manufacturing sector for job creation,” said Vera Songwe, United Nations under-secretary-general and executive Secretary of the Economic Commission for Africa.
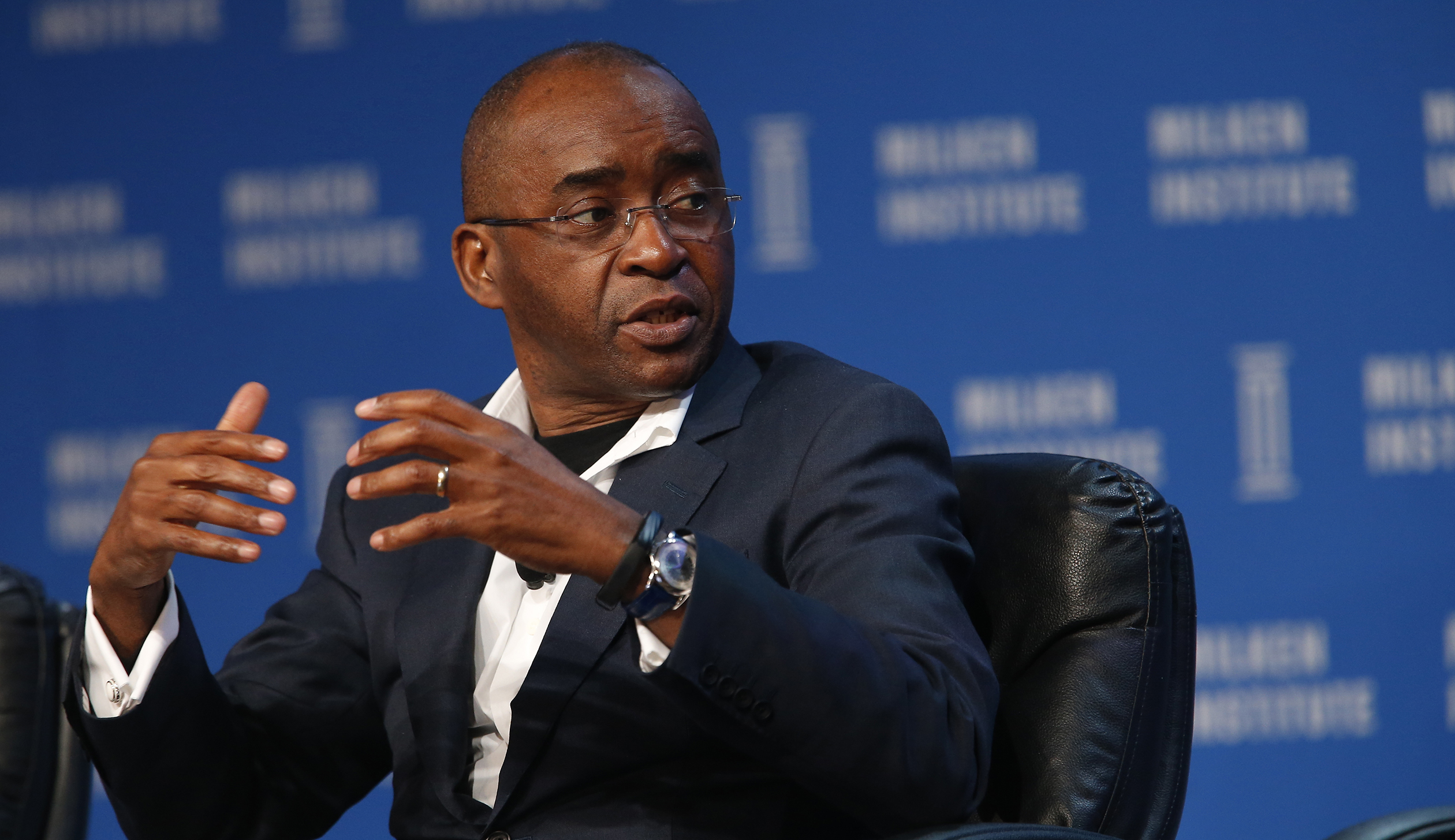
African Union special envoy Mr Strive Masiyiwa, who has been instrumental in securing the vaccines, said the coming on board of Unicef will assist in thwarting a third wave of the deadly coronavirus pandemic that is raging across the continent.
“We are pleased to have Unicef as a strategic partner in the delivery of these vaccines to our member states, as they are extremely experienced in handling and managing vaccines, and a strong and well-established relationship with all AU member states,” said Masiyiwa, who is also the Econet Group founder and chairman.
Established by African leaders, AVAT has spearheaded African efforts on fair equitable access and distribution of vaccines, negotiating vaccine acquisition with pharmaceutical companies to at least 60 per cent of the African population with safe and efficacious vaccines to achieve “herd immunity” by 2022.
“Since the pandemic began, Africa CDC has worked with Covax to ensure that African Union Member States get fair access to Covid-19 vaccines.
“At this critical moment where widespread vaccination is more urgent than ever, we must do all to vaccinate at least 60 per cent of the African population by 2022,” said Nkengasong, Africa CDC director.
The procurement of these vaccine doses has been made possible with the support of the African Export-Import Bank (Afreximbank), which provided a US$2 billion Advance Procurement Commitment (APC) Guarantee facility to Johnson and Johnson on behalf of the AU member states.
The bank also made available direct financing to AU Member States which require funding to pay for the vaccines.
In April 2021, Afreximbank made a down payment of US$330 million to Johnson and Johnson on behalf of the AU member states, as part of the commitment under the Agreement.
“As the financial and ransaction advisers to AVAT on the Johnson & Johnson Agreement, we are pleased to formally welcome Unicef to the partnership and look forward to a fruitful collaboration for efficient delivery of vaccines to African countries,” said Professor Benedict Oramah, President of Afreximbank.
Access to vaccines is the surest way out of the Covid-19 pandemic. Emerging new variants suggest that global recovery will remain elusive if Africa is left behind. Speed and scale in vaccine distribution are imperative for economic recovery.
The AVAT and Unicef partnership will also work to increase procurement and manufacturing on the continent as part of a broader strategy for sustainable health systems and job creation in Africa.
The pandemic has highlighted Africa’s pharmaceutical manufacturing vulnerabilities.
Prior to the pandemic, the continent was only able to manufacture less than two percent of the total medicines needed.
“Access to Covid-19 vaccines has been unjust and unfair, with people in Africa bearing the brunt of this inequality. This cannot continue,” said Unicef executive director Henrietta Fore.
“Unicef is a staunch partner of the African continent with a long history of delivering vaccines everywhere they are needed.
“We are pleased to join this partnership with the African Union and AVAT to maximize supply and access to vaccines.”
The distribution of the J&J vaccines to countries through AVAT Advanced Purchase Agreement is expected to commence this month.

 Slider3 years ago
Slider3 years ago
 National4 years ago
National4 years ago
 Tourism and Environment4 years ago
Tourism and Environment4 years ago
 Opinion4 years ago
Opinion4 years ago
 Special reports4 years ago
Special reports4 years ago
 National4 years ago
National4 years ago
 National3 years ago
National3 years ago
 National3 years ago
National3 years ago