BY METRO
Metro’s foreign correspondent Gergana Krasteva reports from Zimbabwe
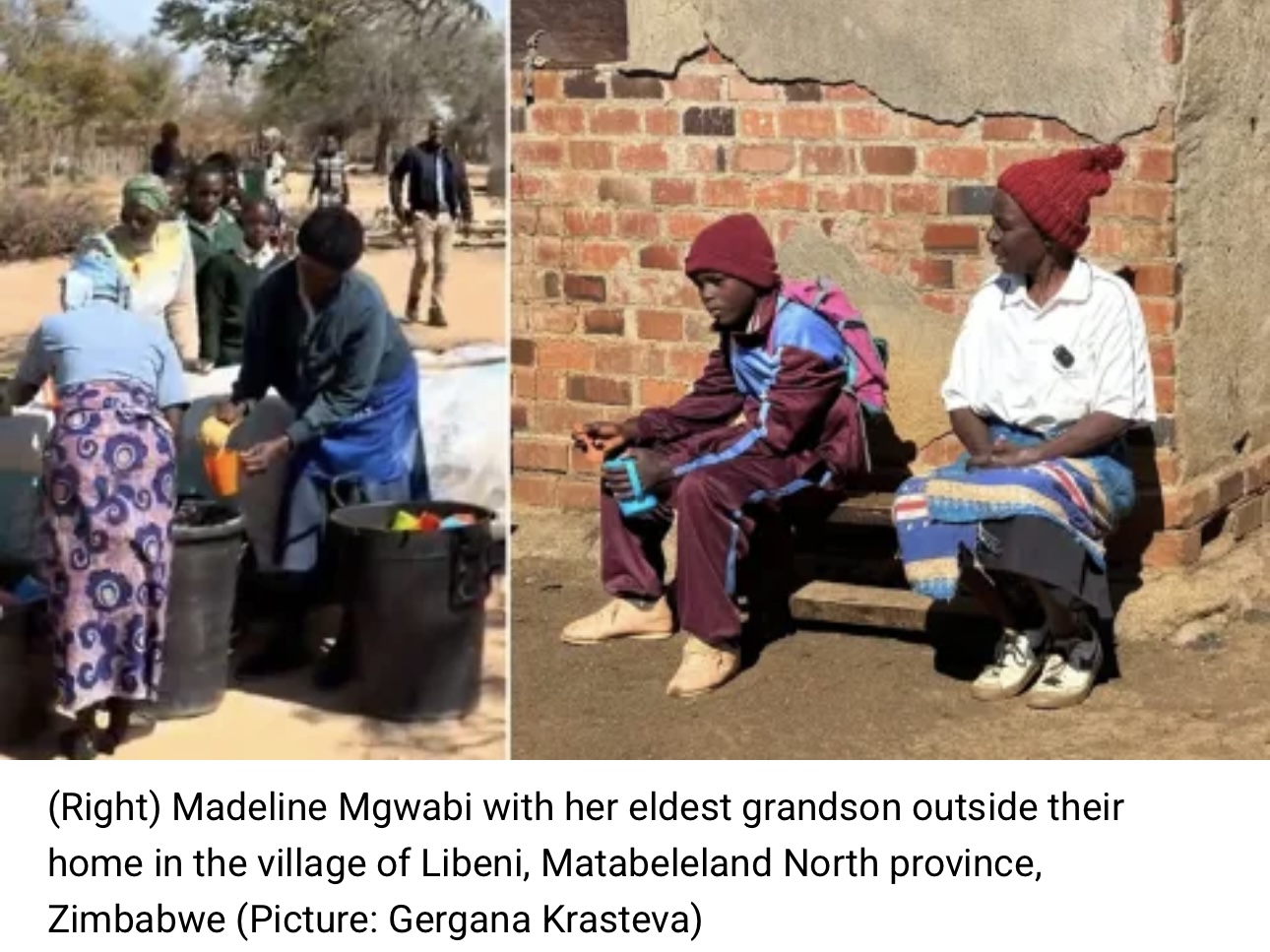
The last time I see Madeline Mgwabi, she is peering through the gates of her crumbling home in western Zimbabwe.
The grandmother-of-three is clutching a single orange that our driver had slipped to her – leftover from the hotel breakfast.
The fruit will have to be split four ways – between her and her grandsons – one of them still a toddler – all of whom she is raising on her own in this godforsaken area in the southern part of Matabeleland North province.
Beside her, on a wooden bench, is her eldest grandson, still dressed in his purple and blue school uniform, steadily scooping gooey porridge from a plastic container.
To put food on the table, Madeline fetches firewood and does odd jobs for neighbours in the village of Libeni, in Umguza District, but it is not enough.
Worst drought in century devastates Zimbabwe
Before droughts robbed the region of water, the grandmother used to farm maize and other Zimbabwean staple crops in her now barren garden.
Gesturing at the dried-up shrubs, she tells Metro: ‘I have lived here for 25 years and each year, the droughts hit us worse and worse.
‘Because of the climate, we often do not harvest anything.’
Her face is hollowed by the years of loss, and her palms are calloused by the decade of grinding in Zimbabwe’s artisanal mines.
What Madeline fears is that her grandsons will eventually have to abandon education in favour of mining to earn a living.
The family’s financial struggle resembles the one of millions of people who have been burdened by the decades of macroeconomic instability, political isolation and now, climate change in Zimbabwe.
Driving through Matabeleland North – where agriculture used to be one of the key economic sectors – Metro witnesses the scars of the climate warming cycle, El Niño, firsthand.
Here, the earth appears to have forgotten what rainfeels like, despite the determination of Zimbabweans to revive what has been lost.
Alongside the road, cattle search for anything to eat – grass, shrubs, any bit of greenery left in a land that has surrendered.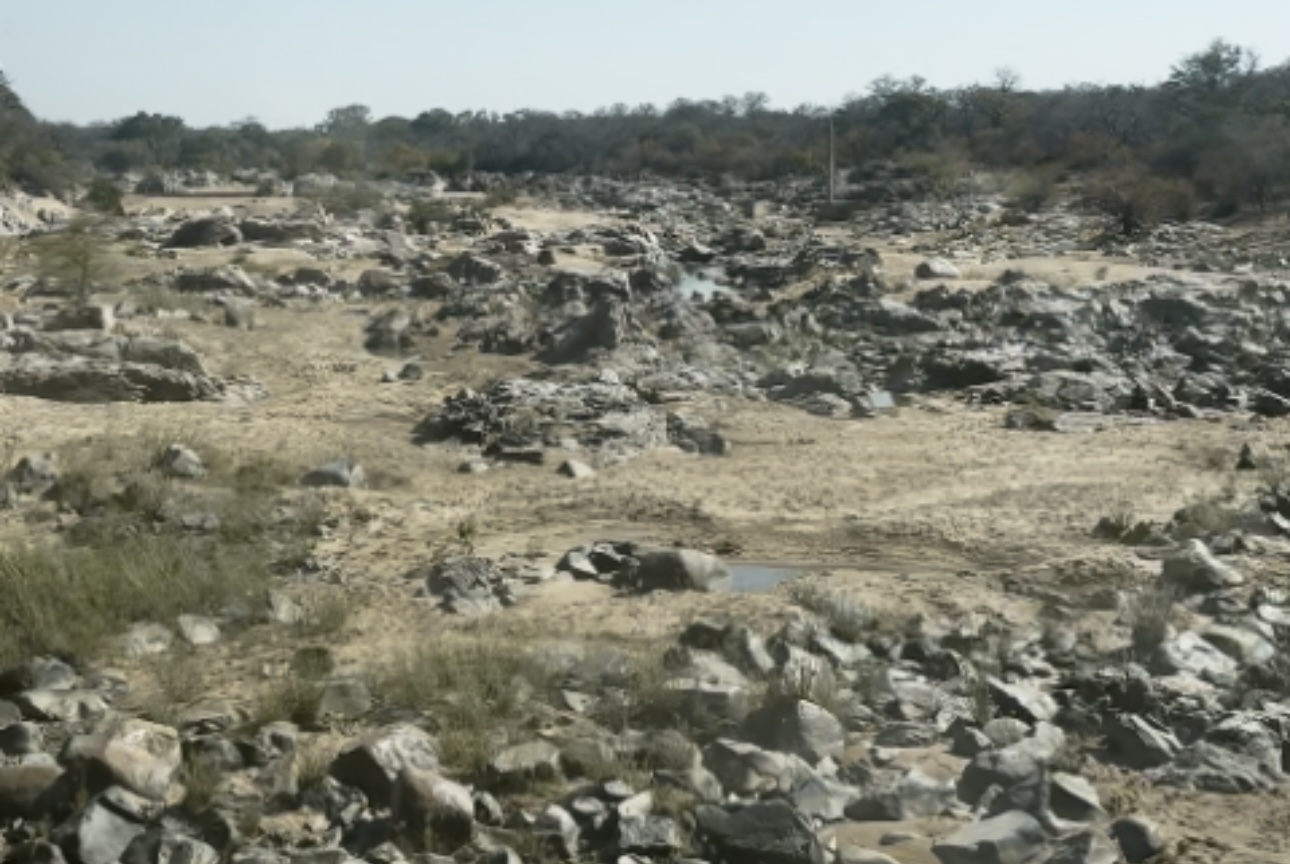
The SUV rumbles past what the driver tells me was, until 2023, the mighty Shangani River that used to nourish the region; now, it is nothing more than a cracked bed of mud and rocks.
Last year, the Zimbabwean president Emmerson Mnangagwa declared a national disaster to tackle the prolonged drought crisis.
Lesotho, Malawi, Namibia and Zambia did so too. Other African nations were also severely affected.
As most households depend on agriculture for food, seven million people in Zimbabwe faced big shortages during the 2024-2025 season, despite improved crops this year.
Boys drop out of school to work in mines
Children have been the most impacted by the droughts – with some opting to drop out of school because their parents cannot provide them with food.
A fifth of all Zimbabwean children aged less than five suffer from chronic malnutrition, with merely 10% of babies aged six to 23 months receiving an adequate minimum diet, according to recent figures.
Hunger is only one part of a vicious cycle that children are trapped in. With households collapsing under the weight of poverty, boys as young as nine leave school to risk their lives in unregulated mines – and girls are married off to provide their parents a brief financial relief.
Girls forced into early marriages for dowry
In Zimbabwe, one girl out of three is already married before turning 18, and more than one out of five has given birth.
Scores of underage brides fall victim to domestic violence and face grave health risks, from early childbearing to HIV.
Although underage marriage is illegal in Zimbabwe and local organisations have been fighting against it, families driven by poverty resort to it.
Lungisani Nyathi knows all too well the dangers his four children face; yet with no steady work and no wages coming in, he feels powerless to shield them.
Gesturing at a makeshift shack, clumsily constructed out of wood and blue tarpaulin, that is his new home, he tells Metro that his wife gave birth just 10 months ago to their baby girl.
‘As a father, I am supposed to provide for my children,’ he shares his fears.
‘If I fail to provide for my daughter when she grows up, I worry that she will have to marry someone very young.
‘It is common for girls to be tied into early marriages due to the financial situation of their families.
One day, our baby girl will have to face the same situation. Young girls are so desperate, they go to bars themselves to search for money.’
Lungisani, who volunteers as a security guard for a borehole that supplies water in Village 5, in Bubi District, wishes to relocate his wife and children to another area so that his boys are not tempted to work in the gold mines nearby.
Wherever schools are located near mining fields, boys are sometimes lured into the pit, under the promise of some money.
After working in a gold mine for six months last year, Lungisani knows all too well that this is not the life for a child.
Describing the conditions as ‘very harsh, because workers are not given any protective clothing,’ he adds: ‘Even the dust was choking us.’
Children in mines is a ‘ticking time bomb’
Khumalo Fanta, deputy headteacher at the Amazwimabili Primary School, shares similar fears for her pupils and says that every year, a few children drop out to work in the mines or to be married off.
She tells Metro that boys, not even in their teens, who work as miners, are swiftly swept into a world of alcohol abuse, without parental supervision.
With what little money they make, they often entice young girls with false promises of a better life – pulling them both into the same cycle of poverty they were trying to escape, before their lives have even started.
Khumalo says: ‘A lot of boys would leave school and go work at the mines. It exposes them to elicit behaviour… There is always alcohol near the mines because it sells fast to adolescents.
‘There is no control as parents are simply grateful that money is coming home, but it is dangerous.
‘It is a ticking time bomb. When they come back, they flash their money… and the girls are attracted.
‘Then they are lost in their behaviour because those boys just get drunk, shouting, they do all sorts of things.’
If children go to school at all, the absence of support systems means that they walk several miles on empty stomachs every morning.
Three million children fed every day
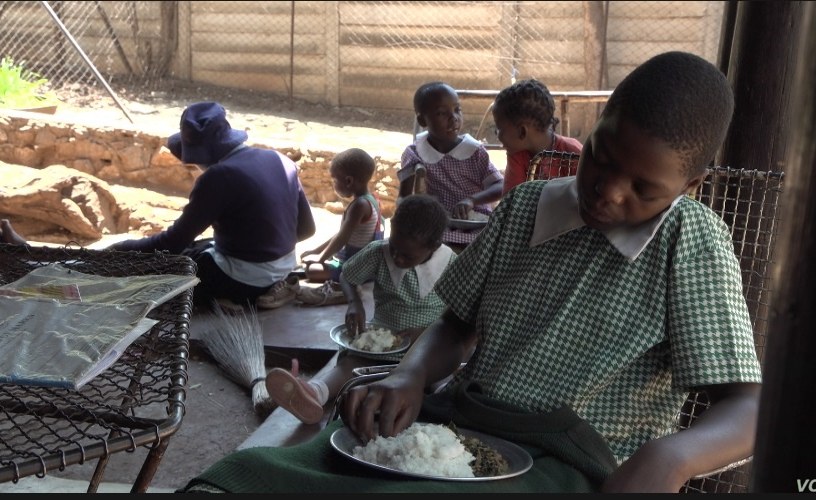
Mary’s Meals, a Scottish-based charity, is working to break that cycle by providing daily school meals for children in early education.
The concept is simple. Mary’s Meals provides food for school, but it is the parents – often the mothers of the pupils – who prepare it and serve it up in between classes.
The promise of a warm bowl of porridge a day has become a lifeline, and sometimes the only meal a child will be guaranteed.
Madeline’s eldest grandson, for example, is one of the pupils part of the programme.
She says: ‘There is nothing more important for my grandsons than going to school and having an education. So having porridge at school is so helpful as it reduces the workload for me.’
Dromoland Primary, the Bubi District of Matabeleland North, is one of the schools with which Mary’s Meals has been working with.
Simeleni Mguni, the headmaster since 2020, told Metro that at the end of last year, there were 255 pupils – but this year there are 279 because of the feeding programme.
‘We enroll new learners every week,’ she says beaming with pride, her smile stretching across her round face.
Before the programme was introduced at the beginning of the school term in 2022, four boys and four girls dropped out because their parents could not feed them.
Simeleni says, regretfully: ‘I know some of the left because they needed to find jobs. Almost all the boys – aged between 12 and 14 – went to search for work in the illegal mines.
‘For awhile, they moved from one gold mine to another, in the nearby area. It is not easy work. If they would find any gold they have to sell it for really meagre amounts of money [as it is not from a registered pit].
‘Two years later, they are now back in school because of Mary’s Meals, and passed their exams recently.’
The four girls – aged between 13 and 14 – are also back in the classroom.
Simeleni said they had left because they did not have period products and were ’embarrassed’ to come to school.
By easing hunger, Mary’s Meals reduces the number of children who might otherwise drop out to work or marry, or just stay at home.
Mary’s Meals has been operating in Zimbabwe since 2018, with the help of a grassroots-based NGO, ORAP.
Working in some of the poorest countries across Africa, Asia, the Middle East, Latin America and the Caribbean, the charity has today announced the grim milestone that it is feeding three million children every day.
Metro travelled to Zimbabwe with the help of Mary’s Meals, a Scottish-based charity feeding children in the country.

 Slider3 years ago
Slider3 years ago
 National4 years ago
National4 years ago
 Tourism and Environment4 years ago
Tourism and Environment4 years ago
 Special reports4 years ago
Special reports4 years ago
 Opinion4 years ago
Opinion4 years ago
 National4 years ago
National4 years ago
 National3 years ago
National3 years ago
 National3 years ago
National3 years ago