BY NOKUTHABA DLAMINI
Nearly two years after Zimbabwe introduced its Covid-19 vaccination programme, some people in rural parts of Hwange district in Matabeleland North are still sceptical about the safety of the vaccines.
Zimbabwe first rolled out Covid-19 vaccines early last year with the country relying mostly on Chinese made vaccines to bring the pandemic that paralysed the economy under control.
Hwange district, where Victoria Falls is located, was one of the areas that were prioritised by the government in the vaccination blitz as it sought to have tourist resorts re-opened for tourists.
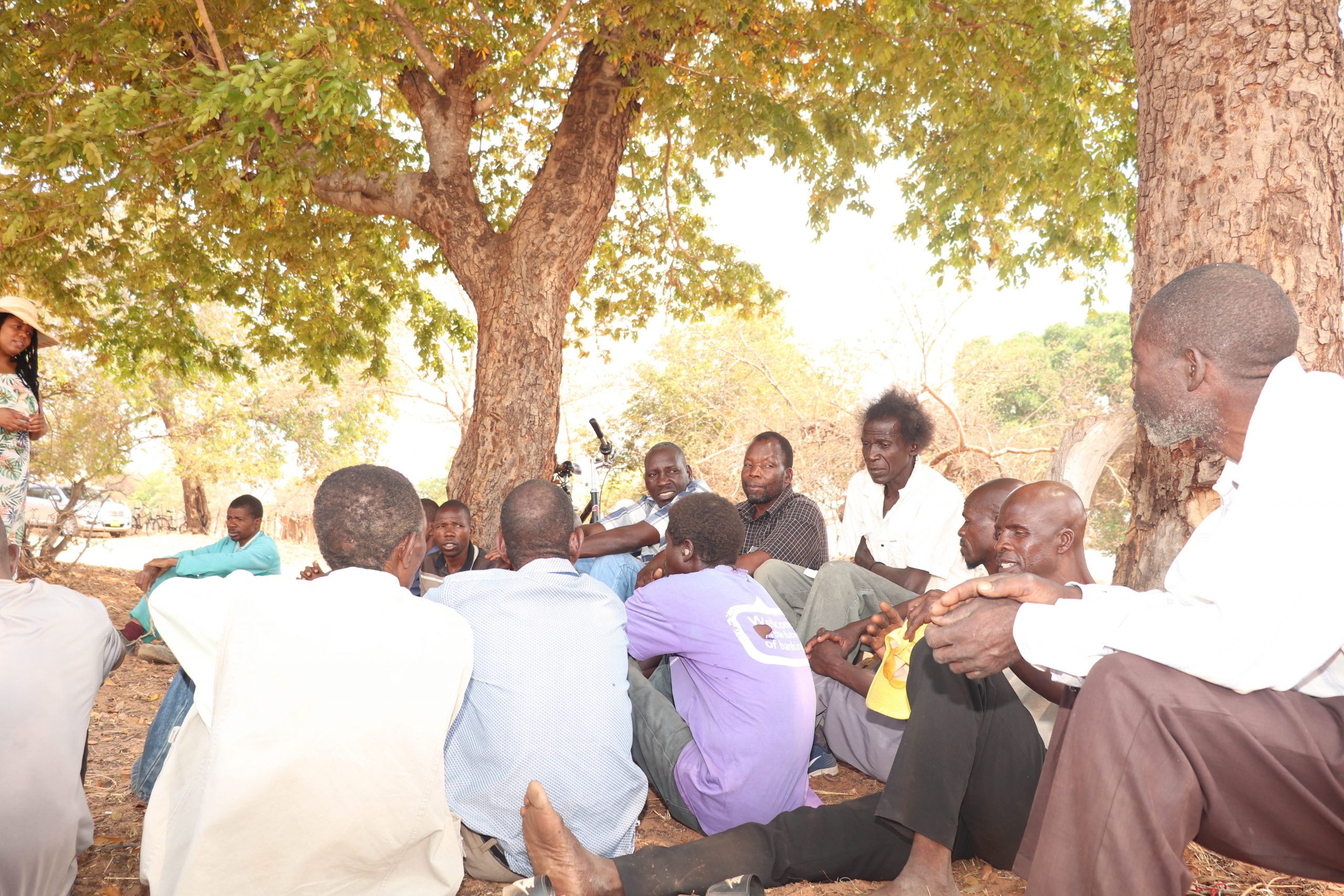
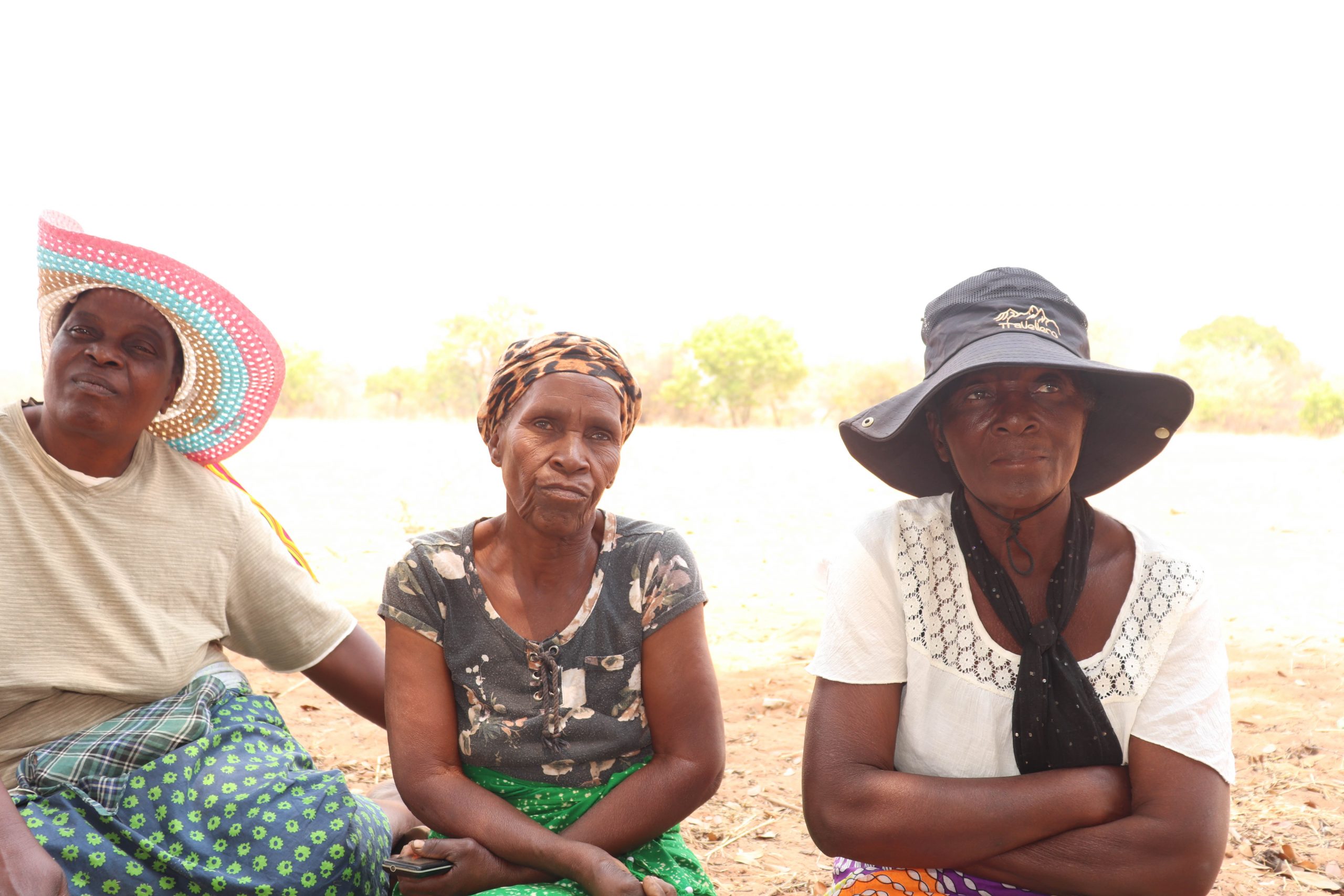
As a result Hwange has the highest Covid-19 vaccination coverage at 80 percent of the population, but three community listening sessions organised by VicFallsLive in the largely rural Hwange West constituency showed that some villagers are still sceptical about the vaccines, largely because of misinformation.
Community leaders said the government did little to counter the misinformation, which is largely blamed on social media and this fuelled vaccination hesitancy.
Hwange villagers, like other people in many parts of Zimbabwe, were victims of misinformation about the vaccines, including allegations that those who got the Covid-19 vaccine will turn into baboons or that the vaccines were part of a scheme to reduce Africa’s population.

Given Moyo, the ward three councillor told VicFallsLive that most people in his area only got vaccinated after they were told that those who were unvaccinated would be barred from using public transport or excluded from government aid programmes.
“Authorities did not bring enough awareness campaigns to rural people on the pandemic and even after the vaccines were found,” Moyo said.
“It was at a time when people were being threatened that they will be barred from accessing public services and during that time, only government run buses were allowed to operate.
“Only those with vaccination cards were allowed into the Zupco buses.
“What complicated the situation was that this was the time when myths about Covid-19 vaccines were spreading and people were being told that if they got vaccinated they were going to turn into baboons’ years later.
“Some said those who got vaccinated will start speaking Chinese languages and give birth to Chinese children.
“We were also told that the vaccines carried an electronic chip that would track and monitor the people.
“People got confused as they were being denied access to public services.
“So they ended up getting vaccinated so as to access shops, banks, and public transport, not that they were convinced that the vaccines were safe.”
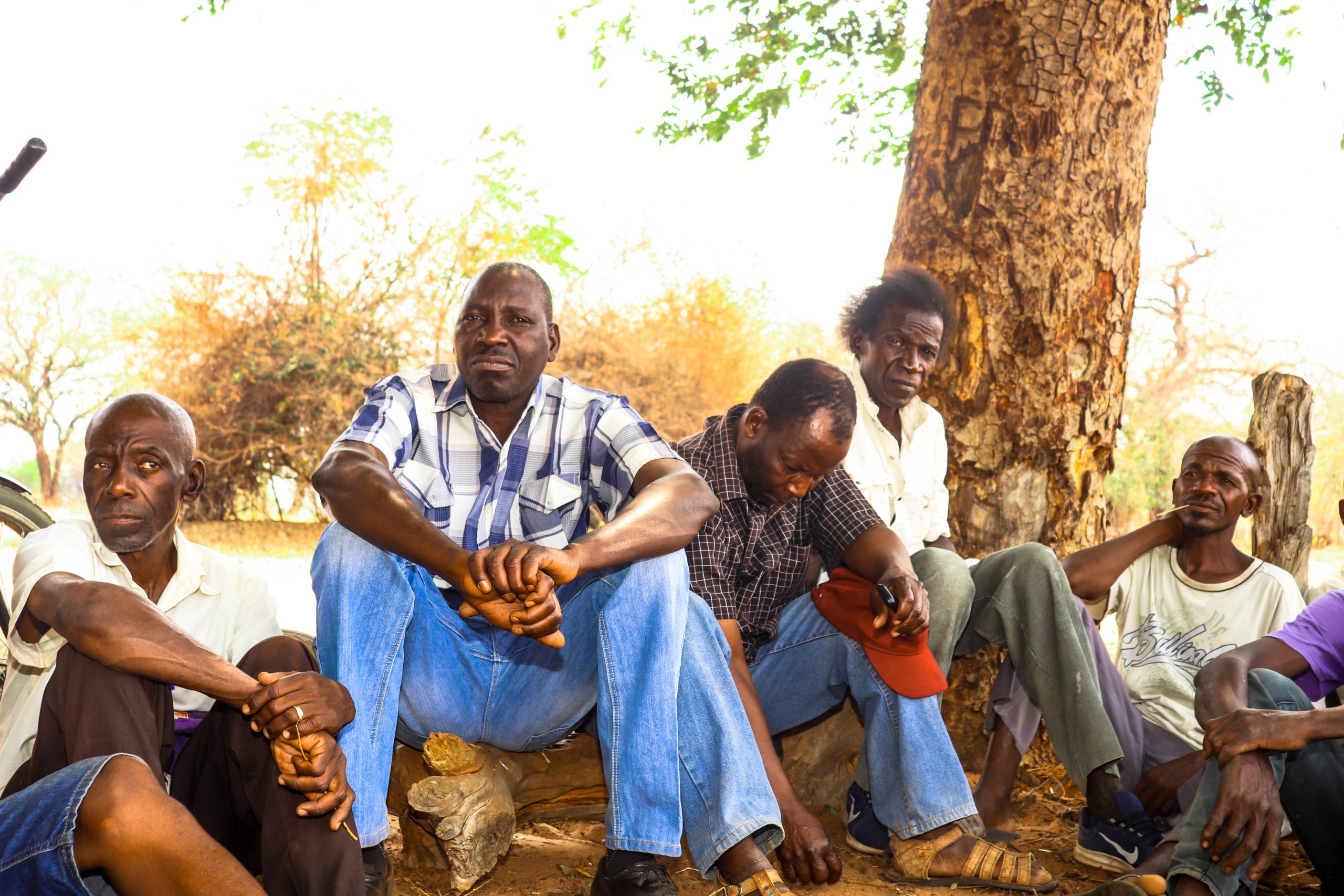
Chief Mvuthu village chairperson Paulos Ntini said misinformation became the biggest hindrance to the Covid-19 vaccination programme.
Ntini said the situation was made worse by the fact that the government had no deliberate strategy to counter the misinformation, which targeted the rural population.

Most parts of Hwange have no access to both the broadcast and print media, which the government relied on to share messages about the Covid-19 vaccination programme.
Community leaders and villagers said some of the dominant myths about Covid-19 vaccines were that they caused infertility and impotence.
“It meant that both men and women were going to lose their sexual appetite,” said BH26 vllage head Jerita Ncube on some of the myths about Covid-19 vaccines.
BH27 village head Tymon Sibanda concurred, adding that: “Some homes were destroyed because people were practicing social distance even in bedrooms.
“We heard that vaccines kill sexual appetite and pregnant women were going to have miscarriages while those who were menstruating were going to bleed non-stop.”
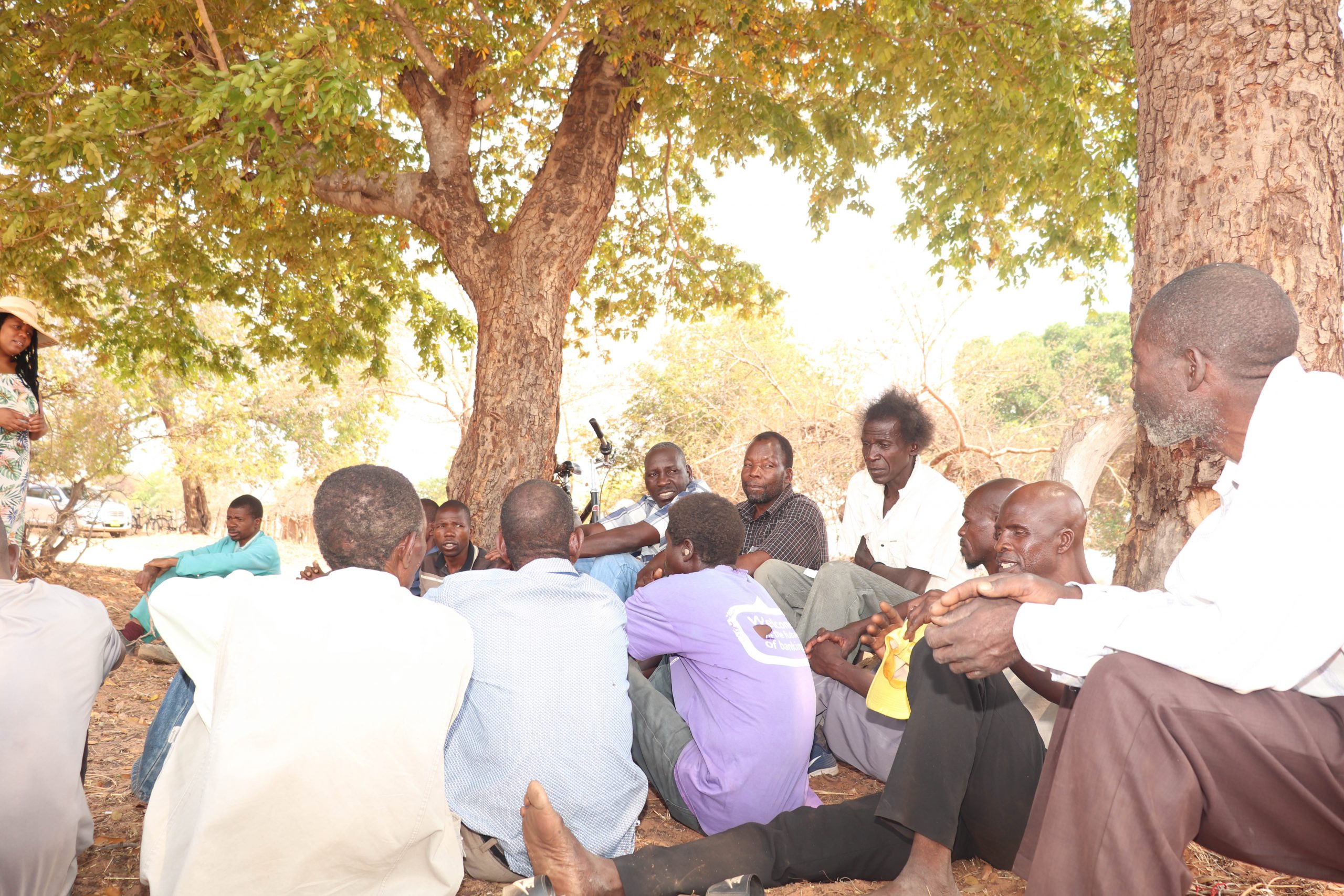
The villagers said scarcity of information from formal channels forced them to rely on social media, which was the major source of misinformation.
“We had a number of local students at Ndlovu Secondary School, who tested positive for Covid-19, but we never saw any government health workers making a follow-up on the case,” said a villager.
“No one came to teach us the elderly on how to nurse those with Covid-19 without getting infected.
“So all these misinformation problems emanated from such neglect.”
Another youthful villager added: “We relied on traditional herbs such as umtshibi whenever our bodies signalled anything related to Covid-19, but no one told us whether that worked or not.
“It was said that Covid-19 was deadly and such herbs treated it as well as garlic.”

Councilor Moyo said whenever he developed Covid-like symptoms, he would drink hot water ‘even though it harmed our throats and was painful to drink’ because they were told it would kill the virus.
Other villagers said they were forced to leave their jobs as they feared contracting Covid-19, which they were told was a ploy to wipe out the African population.
“We were divided even in churches because at some point vaccination cards were required for people to attend church services,” said Flora Ndlovu, an aide to Chief Mvuthu.
“It was a struggle because after getting vaccinated we were branded Satanists because of the vaccine marks.”
Isaac Ntuli, a sports leader in the Chief Mvuthu area added: “In our battle with the devil as Christians, Covid-19 vaccines became a test (of our faith).
“We were confused because vaccines became associated with Satanism and we were told that accepting the vaccines was an evil dedication.
“The fact that the government was coercing people to take the vaccines by threatening to bar them from accessing public services fuelled the myths about Satanism.
“We were also told that this disease was introduced by powerful countries such as China to wipe out Africans as they sought to loot gold and other natural resources without any resistance.”

Sibanda said the Covid-19 pandemic also fuelled corruption even among health workers.
“We saw some people being given Covid-19 certificates with a negative result even after testing positive to the virus after paying a bribe,” he added.
“Even those that would go to Victoria Falls Hospital to get tested so that they can travel to Zambia on medical grounds, they would be told they tested positive until they paid bribes of between US$5 to US$15 for their results to be changed to negative.”

 Slider3 years ago
Slider3 years ago
 National5 years ago
National5 years ago
 Tourism and Environment4 years ago
Tourism and Environment4 years ago
 Special reports4 years ago
Special reports4 years ago
 Opinion4 years ago
Opinion4 years ago
 National4 years ago
National4 years ago
 National3 years ago
National3 years ago
 National3 years ago
National3 years ago