BY NOKUTHABA DLAMINI
Many children in Zimbabwe are born under weight and the country is battling to deal with stunted growth among infants, this year’s Global Nutrition (GN) Report says.
The data on the country’s nutrition profiles said Zimbabwe still has a burden of malnutrition but is ‘on course’ to meet three targets for maternal, infant and young child nutrition.’
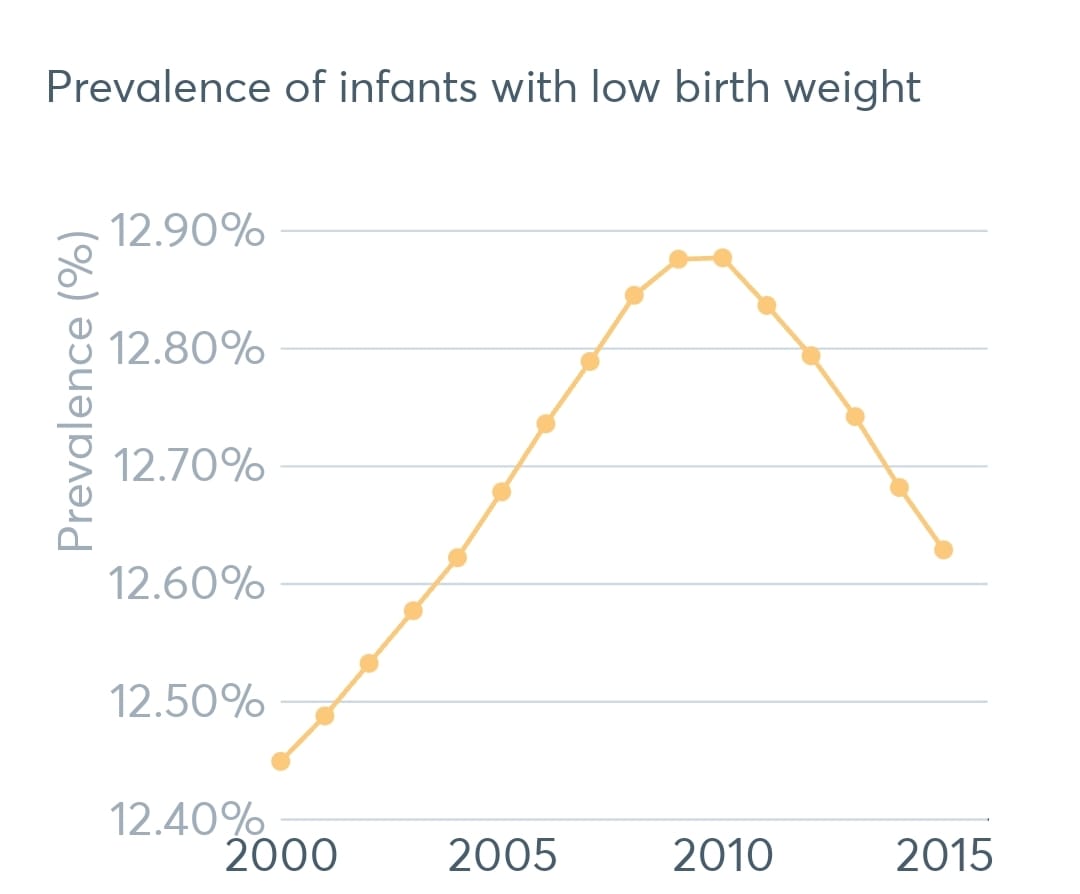
“No progress has been made towards achieving the low-birth-weight target, with 12.6% of infants having a low weight at birth.
“Some progress has been made towards achieving the exclusive breastfeeding target, with 41.9% of infants aged zero to five months exclusively breastfed,” the report released this week says.
Zimbabwe is ‘on course’ to meet the target for stunting, with 23.5% of children under 5 years of age affected, which is lower than the average for the Africa region (30.7%).”
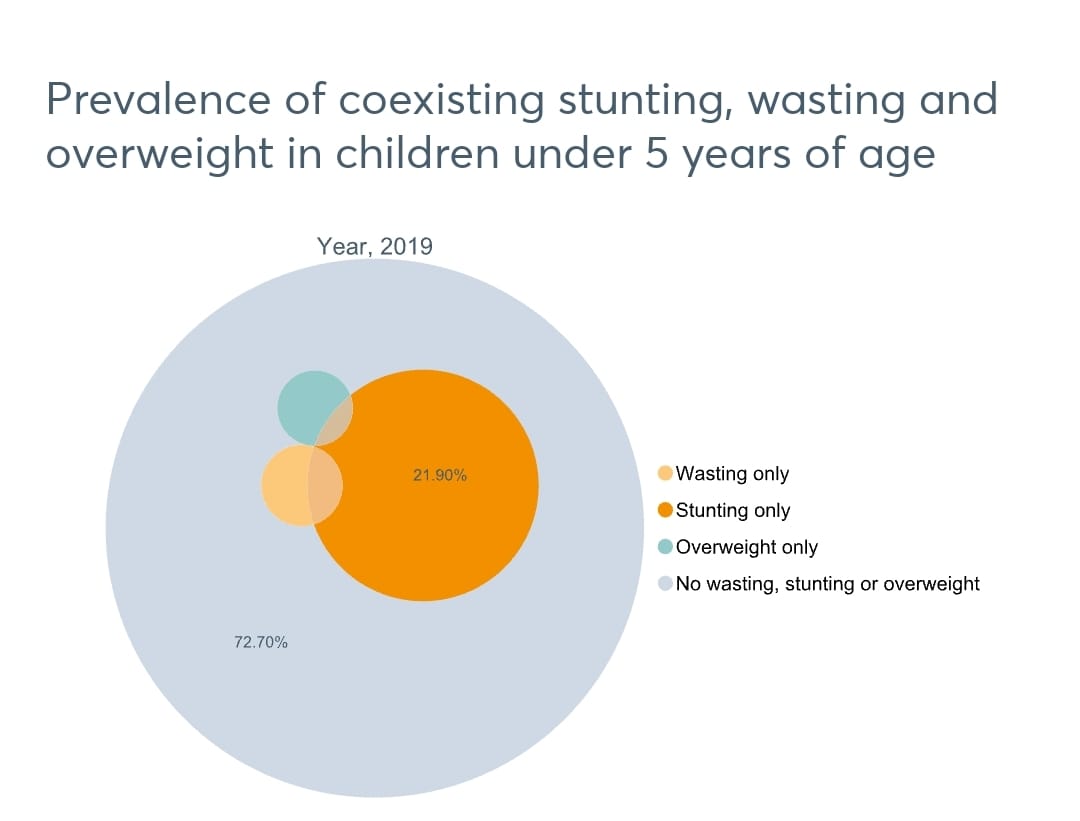
The report says Zimbabwe also missed the target for wasting, with 2.9 percent of children under five years of age affected, which is lower than the average for the Africa region ( six percent).
The report also noted that the prevalence of overweight children under 5 years of age is 2.5%.
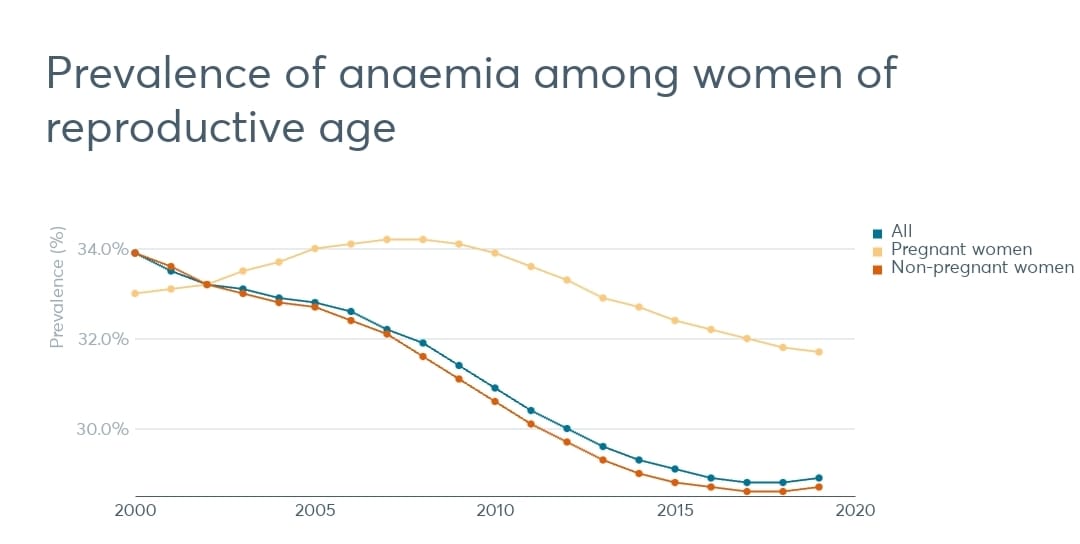
Some progress, however, has been made towards achieving the target of reducing anaemia among women of reproductive age, with 28.9 percent of women aged 15 to 49 years now affected, the report added.
On obesity and diabesity, the report noted that there has been limited progress towards achieving the diet-related non-communicable disease (NCD) targets.
“The country has shown no progress towards achieving the target for obesity, with an estimated 27.9% of adult (aged 18 years and over) women and 5.6% of adult men living with obesity,” the report added.
“Zimbabwe’s obesity prevalence is higher than the regional average of 20.7% for women but is lower than the regional average of 9.2% for men. At the same time, diabetes is estimated to affect 8.1% of adult women and 7.3% of adult men.”
It recommended implementation of policies to reduce the impact of marketing of foods and beverages high in saturated fats, trans fatty acids, free sugars, or salt on children.
Operational policy, strategy, or action plan to reduce unhealthy diet related to non-communicable diseases and policy to eliminate industrially produced trans fatty acids were also among the list of recommendations.

 Slider3 years ago
Slider3 years ago
 National4 years ago
National4 years ago
 Opinion3 years ago
Opinion3 years ago
 Tourism and Environment4 years ago
Tourism and Environment4 years ago
 National2 years ago
National2 years ago
 National3 years ago
National3 years ago
 National2 years ago
National2 years ago
 National4 years ago
National4 years ago






