BY RAY NDLOVU
When Zimbabwean businessman Nigel Chanakira asked 100 chief executive officers at a seminar in Harare on January 27 if they were willing to use the local currency, only one raised his hand.
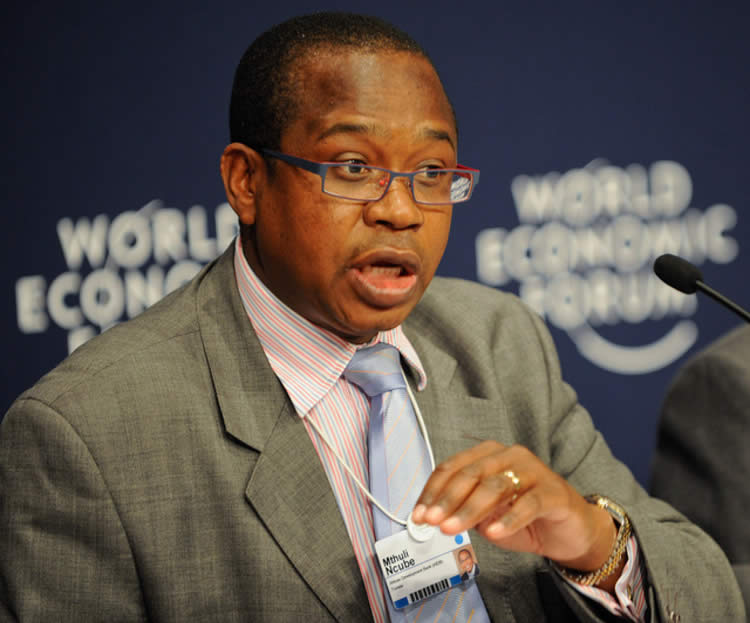
That reluctance is a stark demonstration of the government’s failure to win confidence in the Zimbabwe dollar, the reintroduction of which Finance minister Mthuli Ncube has staked the stagnating economy’s recovery on.
For the second time in two decades, Zimbabweans are abandoning their local currency.
At restaurants, a simple request for “the rate” sees one’s bill halved if it’s met in hard currency, and supermarkets openly offer discounts for goods purchased in United States dollars.
The government paid public workers their Christmas bonuses in dollars, and the revenue service collects a third of its income in greenbacks.
“We can’t deny the reality,” Chanakira, the founder and former CEO of now-closed bank Kingdom Financial Holdings Ltd., said in an interview.
“When you get the Zimbabwe dollar you spend it quickly. No one wants to save in that currency.”
Between 2009 and 2019, Zimbabwe’s economy was dollarised after hyperinflation led the government to print trillion-Zimbabwe dollar notes before abandoning its currency, leaving the country’s name synonymous with economic malfunction.
While the subsequent dollarisation tamed price growth, it hurt businesses as neighbouring countries using their own depreciating currencies undercut Zimbabwean manufacturers.
“Zimbabwe had become uncompetitive by 2013 and was burdened by an expensive workforce,” John Legat, CEO of the country’s oldest brokerage, Imara Asset Management Ltd., said in a note to clients.
In February 2019, the government dropped a peg that kept a precursor of the Zimbabwe dollar at parity with the US dollar.
In June, it was rechristened the Zimbabwe dollar and use of foreign currency was briefly outlawed.
Today the currency trades at 115 to the greenback, and more than twice that on the black market.
While inflation slowed from a 12-year high of 837 percent in July 2020, it was at 61 percent in January, still rapidly eroding the value of the local unit.
Officials including Ncube, a former Oxford University lecturer, and Reserve Bank of Zimbabwe Governor John Mangudya, said government policy is to stick with use of the Zimbabwean dollar.
“The country is not re-dollarising,” Mangudya said in a interview on January 17. “We need to find a home for our currency.”
Ncube and his ministry didn’t respond to requests for comment.
Alois Burutsa, the lone defender of the Zimbabwe dollar at Chanakira’s meeting, said in an interview that “without our own currency, our exports become uncompetitive.”
He’s general manager of Buy Zimbabwe, an organisation that promotes local goods.
Capitulation
Yet central bank figures show that 44 percent of transactions in the country are conducted in greenbacks.
The American currency is used to pay for everything from fuel to food, passports, medicines and school fees.
Econet Wireless Zimbabwe Ltd., the country’s largest mobile phone operator, offers additional airtime and data if purchases are made in US dollars.
With the Zimbabwe dollar untradeable outside the country, companies need foreign currency to pay for imported equipment, consumer goods, and to placate an increasingly dissatisfied workforce.
And it’s not only businesses that are seeking alternatives to the local currency.
The government itself is increasingly finding it has to pay in US dollars if it wants to get things done.
Already it’s told public workers that they’ll be paid partly in hard currency this year.
According to Imara, the brokerage, 45 percent of infrastructure contracts are being met in dollars.
“Dollarisation is the ultimate outcome of a failed economic policy,” said Gift Mugano, executive director at Africa Economic Development Strategies, a Harare-based consultancy.
The Zimbabwe dollar “will be in the graveyard” by June, he predicted. Imara says it’ll be largely obsolete by the end of the year.
Chanakira was more optimistic: he said the currency could survive for another two years. – Bloomberg

 Slider3 years ago
Slider3 years ago
 National4 years ago
National4 years ago
 Tourism and Environment4 years ago
Tourism and Environment4 years ago
 Special reports4 years ago
Special reports4 years ago
 Opinion4 years ago
Opinion4 years ago
 National4 years ago
National4 years ago
 National3 years ago
National3 years ago
 National3 years ago
National3 years ago