BY GAMUCHIRAI MASIYIWA/ EVIDENCE CHENJERAI / LINDA MUJURU
Growing up, Emmanuel never received any of the vaccinations that Zimbabwe requires children to get, such as the polio vaccine and the Bacillus Calmette-Guérin inoculation, which protects against tuberculosis.
His parents were members of an Apostolic sect that rejects conventional medicine and puts its faith in God for healing.
Whenever Emmanuel got sick, the members of his church would pray for him, and he avoided going to doctors and hospitals for treatment.
“God spoke to our chief prophet a long time ago and told us not to seek medical attention, because we can get protection from all illnesses through prayers, and this is what we believe in,” Emmanuel says.
Now, as an adult, he is continuing that tradition with his own family.
The Zimbabwean government has launched its campaign to vaccinate the public against the coronavirus.
But Emmanuel and thousands of other members of Apostolic communities across the country are choosing not to get vaccinated — a decision that threatens to undermine the government’s efforts to protect the public and end the pandemic.
“We were prayed for, but were told [by the head of our church] to make a personal decision on whether to get vaccinated or not,” says Emmanuel, a member of the Johane Masowe Chishanu Apostolic Church, who requested that his last name not be published because he feared retribution for opposing the government’s vaccination policy.
Neither he nor his three wives or seven children, who range in age from 9 to 18 years old, will get the vaccine against Covid-19, the disease caused by the coronavirus.
“I made a choice for me and my family that we will not get vaccinated for personal reasons,” Emmanuel says.
The government’s vaccination campaign began in February.
Initially, front-line workers, elderly citizens, people with chronic health conditions, and other high-risk groups received priority, but vaccinations are now open to the entire population.
More than 750,000 people have received a first vaccine dose, according to the Ministry of Health and Child Care.
Since the start of the pandemic, there have been more than 46,000 confirmed Covid-19 cases in the country and more than 1,700 deaths.
Infections have started to creep up in recent weeks, and the government has issued lockdowns in some hot spot areas.
Officials still have a long way to go to achieve the country’s goal of vaccinating 10 million people, or 60% of the population, in order to reach herd immunity.
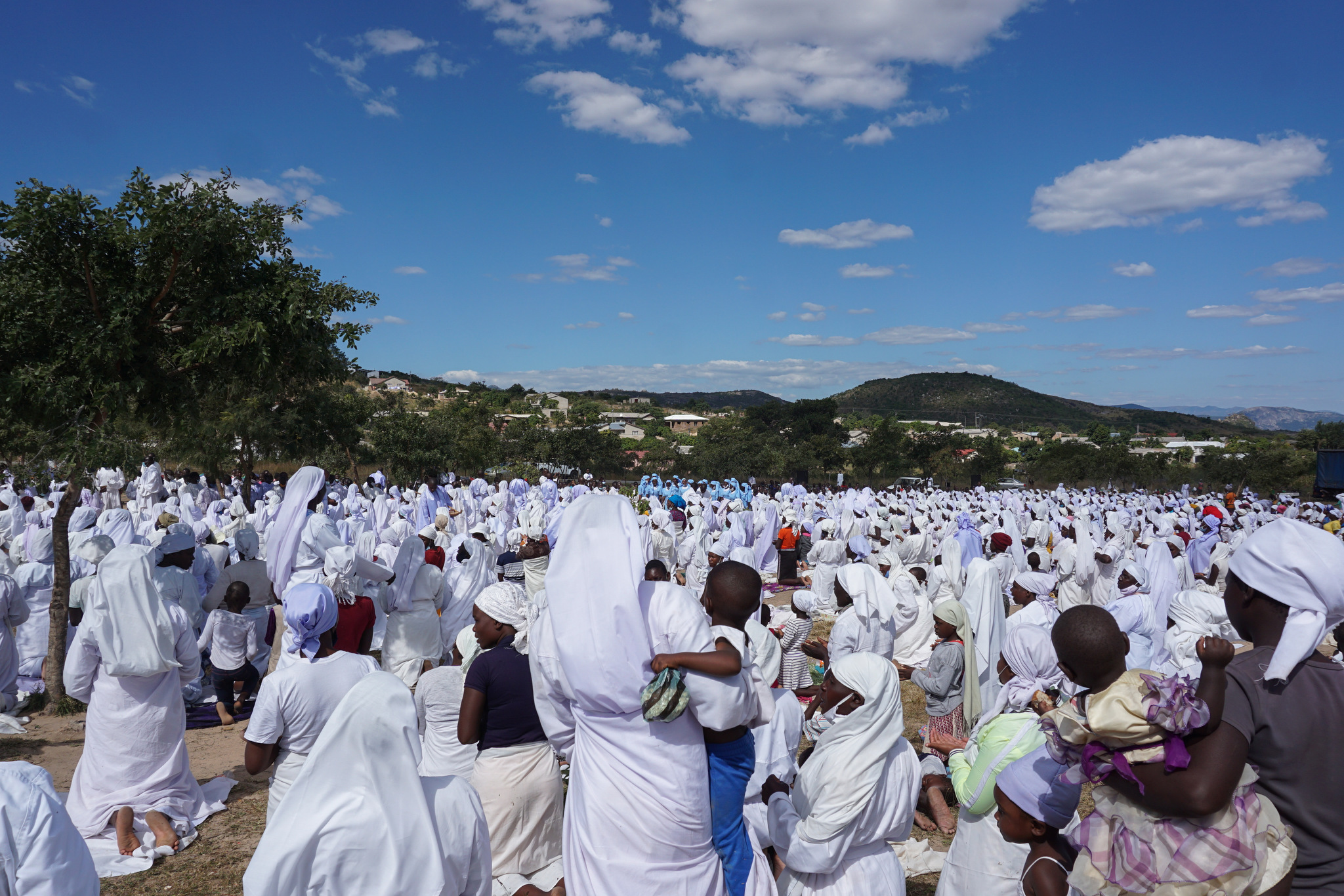
Vaccine hesitancy among the Apostolic community in particular represents a significant challenge.
One-third of Zimbabwe’s population belongs to Apostolic religious groups, tied to Christianity, and leaders of Apostolic churches hold significant sway in society.
A survey conducted last year by the Zimbabwe College of Public Health Physicians found that while 50% of Zimbabweans would accept the vaccine, 30% were unsure about it, and 20% would reject it.
“Religion has always been highly influential when it comes to public health decisions,” said Grant Murewanhema, an epidemiologist and public health physician.
“With regards to Covid-19 vaccination in Zimbabwe, some outspoken religious leaders with very huge followings have spoken against Covid-19 vaccines, associating them with the devil’s intention to destroy mankind.”
Beyond concerns about vaccines and broader religious objections to conventional medicine, researchers have also noted that corruption and lack of trust in the government may contribute to vaccine hesitancy among Zimbabweans.
Agnes Mahomva, chief coordinator of the national response to the Covid-19 pandemic in the Office of the President and Cabinet, says the government is holding workshops and outreach sessions with religious leaders in an effort to overcome opposition to the coronavirus vaccine.
“We are engaging every religious sector to make sure that as they preach to their followers, they are also promoting vaccination,” said Mahomva.
“The good news is we have had a number of religious leaders coming to get vaccinated.”
Chipo Dzingai, the chief adviser of an Apostolic sect in Harare, said the members of her congregation don’t oppose vaccines, including the coronavirus vaccine, and that members of the public should follow the government’s health advice.
“We understand that there are things that require spiritual guidance and others that do not need that guidance,” she said. “We just have to follow the experts in the field. All coronavirus measures that are being implemented are not meant to harm us, but to protect us.”
Andby Makururu, founder of Johane the Fifth of Africa Apostolic Church, agrees that vaccines will help curb the spread of the coronavirus. He’s planning to be vaccinated himself and says he’s advising members of his congregation to do so as well, though some are still hesitant.
“As a church leader, I encourage the people of Zimbabwe to take the vaccine,” he said.
Mahomva says the government respects individual religious views but that church leaders and members of the public damage the country’s overall efforts to protect public health when they speak out against vaccines. She says she hopes more religious leaders will help spread the message that vaccines are safe and effective.
“Individuals have their beliefs,” Mahomva said. “But we work on communicating the right information, the right science, and to get them to come on board, so that their followers can get the vaccination which they all need.” – Global Press Journal


 Slider3 years ago
Slider3 years ago
 National4 years ago
National4 years ago
 Tourism and Environment4 years ago
Tourism and Environment4 years ago
 Special reports4 years ago
Special reports4 years ago
 Opinion4 years ago
Opinion4 years ago
 National4 years ago
National4 years ago
 National3 years ago
National3 years ago
 National3 years ago
National3 years ago