BY DERICK MATENGARWODZI
For months, the idea of her crops being unable to pass another night in the field unperturbed while she dozed indoors rattled Flora Mangwana so much.
These days, the 40-year old farmer sleeps in a makeshift hut outside her home in Siyalwindi, northwestern Zimbabwe.
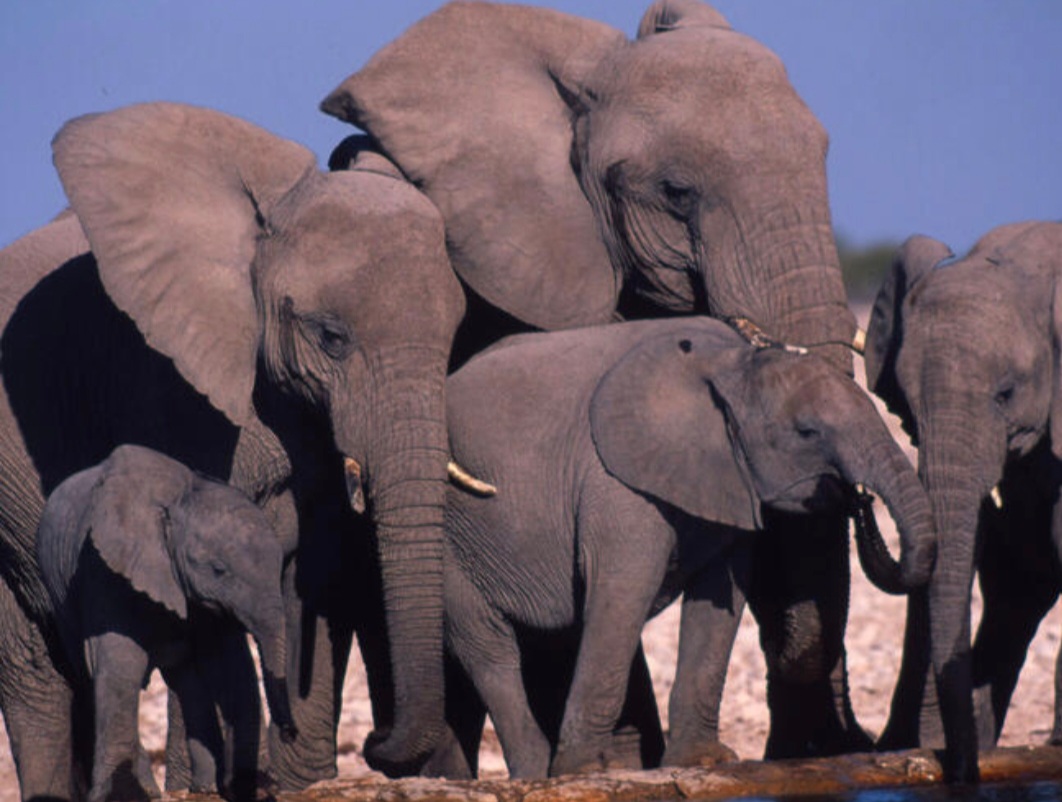
For more than a dozen years now, herds of elephants from the nearby Hwange National Park invade her family plot every other night, devouring the planted maize before it reaches maturity.
That has often left Mwangana, her family’s breadwinner, scrambling to find other food sources to feed her family of six. Ahead of harvest this April, she is worried about a repeat scenario.
“The elephants are coming to our fields in large numbers and we are not going to harvest much this season,” she said.
“Every year, we don’t harvest much because of the elephants. This year, there was little rainfall and elephants are still becoming a big problem, destroying our fields.”
The Hwange National Park is the biggest wildlife reserve in the southern African nation.
In 1928, it was declared a game reserve. Stretching over 14,600 square km and located in the eastern part of the Kalahari Desert, a low rainfall area, it is home to more than 100 mammal and 400 bird species.
During the dry season, the competition for food and water intensifies, resulting in conflicts among the animals.
For years, some of these animals, the elephants, have also been straying into residential areas around the park.
The invasion has led to loss of crops on farmland and lives across the country.
Things have worsened as the elephant population in the game park increased over the years to more than 50,000, far beyond its holding capacity of 10,000, Zimbabwe Parks and Wildlife Management (ZimParks) told the BBC.
In 2020, there were more than 50 injuries and 60 deaths due to growing wildlife-human conflict, according to ZimParks’ website.
It was an increase of more than fifty percent from the previous year.
In search of good pastures and water holes, the villagers drive their livestock into the game park.
Thomas Tshuma (47), a cattle herder has encountered elephants while tending to his livestock in the game park.
“Each time we go into the game to herd our livestock, the elephants are harassing us, attacking and chasing away our livestock at watering holes and pastures,” Tshuma told Al Jazeera.
“The grazing lands are now scarce and we have to look for better pastures to feed our animals.”
To protect their crops, the villagers have formed watch groups to scare away the elephants using primitive weapons and bonfires.
When the animals emerge from the park, the watchmen start beating metal tins loudly to frighten them.
But experts also say that this human activity is part of the problem.
“Land use change and continuous human encroachment near and sometimes in protected areas is the driving factor to the increase in Human-Wildlife Conflict”, said Shamiso Mupara, executive director of Mutare-based nonprofit Environmental Buddies Zimbabwe.
“And it likely results in both parties suffering.”
The increase in demand for land use around Hwange has seen communities encroaching on the game park.
“Before the conflicts started, there was a fence dividing the community and the park. However, it was removed and the elephants have access to the community farmlands,” said Ndlelende Ncube, the founder of Tikobane Trust, a Hwange-based conservation volunteer group.
“Also, the increase in population has resulted in the occupation of buffer zones, sometimes a kilometre wide, resulting in conflicts in 27 villages.”
Survival of the fittest
Due to poor rainfall, the current farming season is likely to yield a poor harvest even as the elephants continue to launch regular raids.
So the villagers are doubling down on crop protection, saying farming as a primary source of livelihood in Siyalwindi is being threatened.
“We don’t sleep in our homes at night, we stay awake trying to keep away the elephants that are coming for the little crops we have,” Mangwana added.
Others have resorted to trapping wild animals for meat or for sale of their body parts to poachers.
ZimParks, which manages the country’s national parks, said it is trying to “create a balance between people and wildlife”, according to Tinashe Farawo, a spokesperson for ZimParks.
“Both the animal and human populations are increasing.”
“Communities who share borders with parks must desist from herding cattle in the parks because their livestock is at risk of contracting diseases and being attacked,” added Farawo.
Previous studies done in the Kruger National Park in neighbouring South Africa to test the repellents have proved that “elephant repellents, chili bombs and beehive fencing are effective in deterring elephants,” according to Mupara.
Last year, Tikobane Trust tested an elephant repellent it made with the help of local advocacy groups, in one village.
The main ingredients were cow dung, water and garlic. It proved to be a “success, repelling elephants from 200 meters away”, said Ncube.
There also seem to be concerted efforts to reduce poaching through skills training and entrepreneurship education for communities near the parks to aid them in participating in the tourism value chain.
Farawo said the villagers are benefitting from Communal Areas Management for Indigenous Resources (CAMPFIRE), a government programme to support community-led development.
Government officials said the funds from the programme are used for development purposes, such as building schools, clinics and roads.
However, some farmers say the perennial losses incurred by the animals trampling on their crops are having a toll on them and they see little direct benefits from the CAMPFIRE funds.
Community members, including Mangawana and Ncube said their neighbours appointed to the committees do not know how it works because they do not run the project.
For example, when a rowdy elephant is shot by ZimParks, communities allegedly get only a small share, Ncube said.
Last year, Dete, another affected area, reportedly received less than US$100 payout, he said.
After years of confronting the elephants, Mangwana is running out of patience and wants quick solutions, rather than new policies and programmes.
“The elephants should rather be taken away from the area,” she said. “We are losing and we are under a lot of stress because we are not sleeping at night.
“The CAMPFIRE funds are only benefitting a few people who are administering the programme.” – Aljazeera


 Slider3 years ago
Slider3 years ago
 National4 years ago
National4 years ago
 Tourism and Environment4 years ago
Tourism and Environment4 years ago
 Opinion4 years ago
Opinion4 years ago
 Special reports4 years ago
Special reports4 years ago
 National4 years ago
National4 years ago
 National3 years ago
National3 years ago
 National3 years ago
National3 years ago