BY EZRA TSHISA SIBANDA
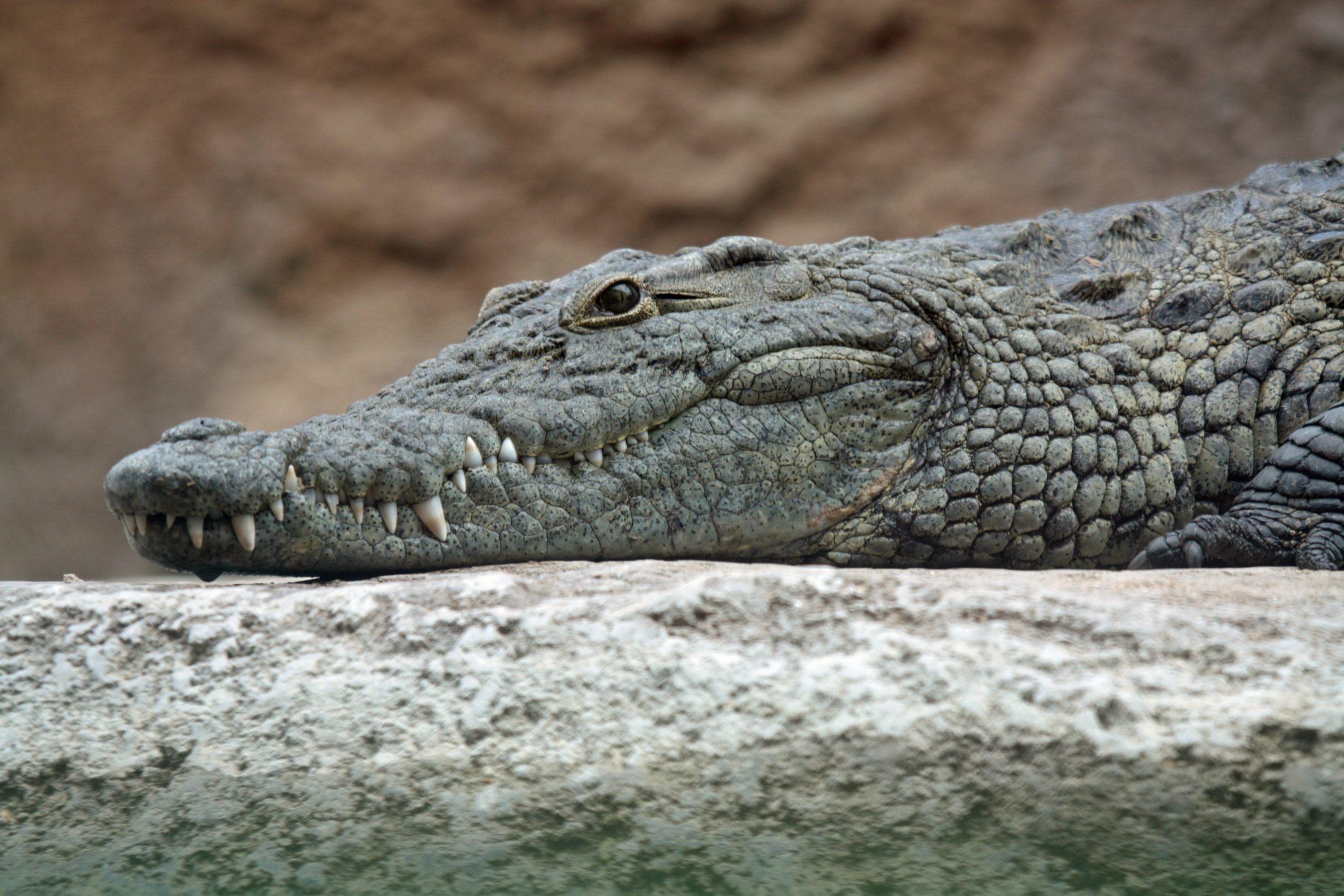
A 53-year-old Bulawayo woman says she escaped from the jaws of a crocodile in Kana River, Matabeleland North, by punching its nose while appealing for divine intervention.
Tholiwe Moyo, who was in company of her sister and two other villagers, were attempting to cross the flooded river recently when she was bitten by the crocodile, which tried to drown her.
The mother of five children fought the reptile off after recalling some childhood advice from village elders that one has to hit it on the nose to scare it. That saved her life.
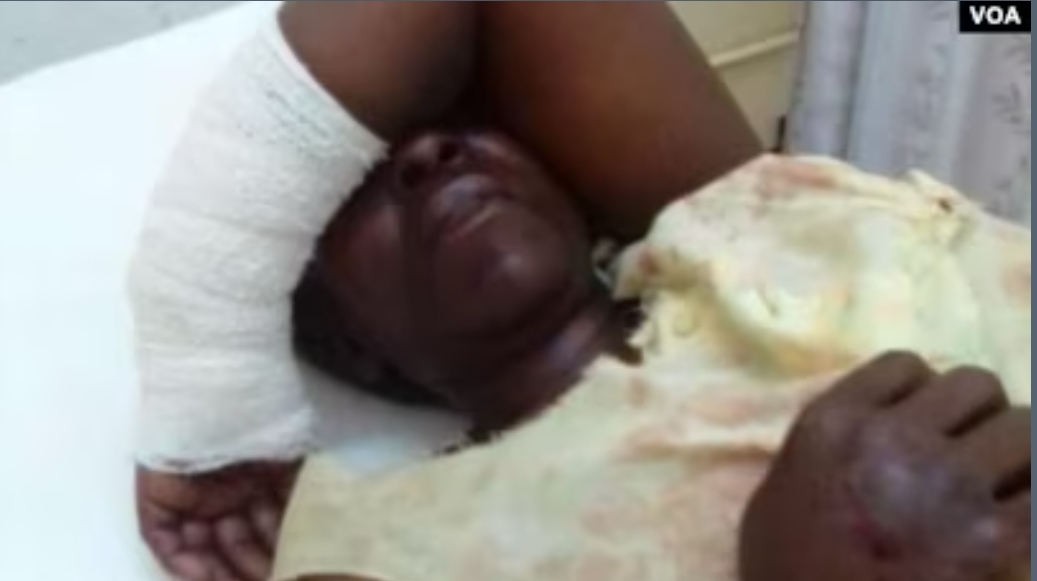
Moyo, currently in a stable condition at Mpilo General Hospital in Bulawayo is nursing serious injuries on her hands, legs and other parts of the body.
“The crocodile attacked me when I was crossing the river with some villagers, who included my 72-year-old sister,” she said.
At first we all thought that someone was throwing stones at us but realized within a minute or so that something had a tight grip on my body.
“ I then realized that it was a crocodile trying to pull me to the deepest part of that section of the river. I screamed for divine intervention.
“While the crocodile was trying to drag me, I recalled what elders related to us when I was growing up.
“We were told that if you punch the crocodile on its nose, it will let you go. I did exactly that while it tried to drown me. I punched it several times on its nose.”
She says the crocodile tried to kill her. “It broke my arm, bit my legs and buttocks and other parts of my body.
“I was also determined to live. So, I punched it hard while screaming for help. It finally let me off.
“ I then crawled towards the banks of the river and my sister and others pulled me to safety.
“By that time, they were carrying sticks and other objects they could lay their hands on in order to push it off.”
The crocodile was not done yet as it attacked, killed and ate the family’s dog, which was trying to swim to safety too.
“It’s sad that our dog is gone but I’m happy that I survived.”
Moyo is in serious pain. “The crocodile wanted to bite my hand off. The left hand is not functioning well as of now.
“My left leg is also seriously injured and the right leg up to my buttocks it’s in bad shape.
“I’m happy that my councillors, Member of Parliament, women’s groups and others have visited me here to show their sympathy and support. I appreciate it a lot. They gave me a lot of fruits.”
Zimbabwe is currently experiencing heavy rains and conservation groups are warning that the rains and flooded rivers have resulted in crocodiles turning up in places where they are least expected.
Late last year, Majaha Ndlovu of Silobela was attacked and eaten by a crocodile while he was fishing with his son, Siphatho Ndlovu.
Siphatho will never forget this day. “We were fishing along Gwelu River when my father dropped his hat and tried to retrieve it from the river.
“All of a sudden a crocodile attacked him and drowned him. The only thing I saw thereafter were pools of blood on the water surface,
“That was the last time I saw my father alive. He was attacked and eaten by that reptile.
“I tried to cry for help while it was attacking him but there was nobody in sight to assist him.
“That pains me a lot and it haunts me. I remember him screaming for help but I could not save him. He died a very painful death.”
National Parks and Wildlife Management authorities say crocodiles are killing people more than any animal, including elephants. – VOA

 Slider3 years ago
Slider3 years ago
 National4 years ago
National4 years ago
 Opinion3 years ago
Opinion3 years ago
 Tourism and Environment4 years ago
Tourism and Environment4 years ago
 National2 years ago
National2 years ago
 National3 years ago
National3 years ago
 National2 years ago
National2 years ago
 National4 years ago
National4 years ago


