BY JASON BURKE
Zimbabwe’s ruling Zanu-PF party may be facing an uphill struggle to secure a clear victory in elections due next year after a new opposition party made significant gains in byelections last weekend, raising concerns of new political instability and possible violence.
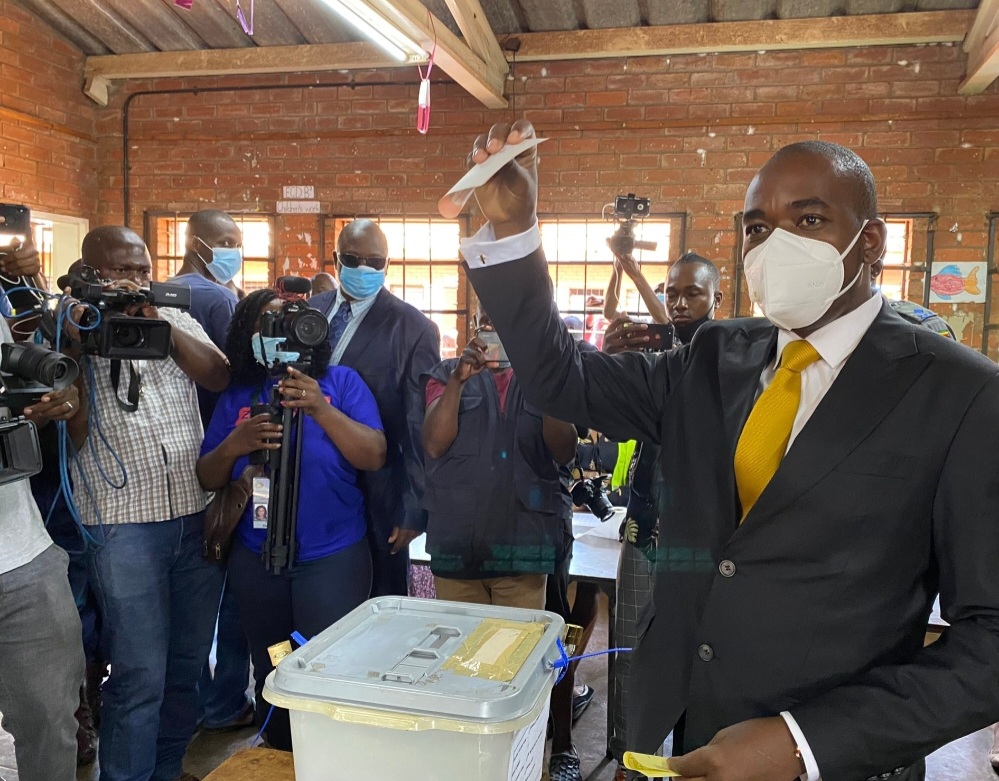
The Citizens Coalition for Change (CCC), which was only founded in January, won 19 out of 28 parliamentary seats in polls widely regarded as a test run for the 2023 presidential election.
In 2018, a fractured opposition came thin one percent of forcing President Emmerson Mnangagwa, who took power following the fall of President Robert Mugabe, into a runoff. The vote was marred by allegations of rigging.
The CCC is led by Nelson Chamisa, who described the weekend’s results as a “landslide”.
“There is nothing that will stop us from forming the next government … Yes challenges are there. Electoral reforms must be implemented, and we have said those reforms have to be put in place,” Chamisa told reporters in Harare earlier this week.
Analysts say the opposition in Zimbabwe has largely unified around Chamisa, putting an end to the worst of the internecine bickering that undermined its previous efforts to win power. The gains made by the CCC at the weekend suggest a tight battle next year, with Mnangagwa likely to be forced into a run-off that he could lose.
Though the CCC won most of the urban vote, taking 75 of the contested 122 municipal seats, it failed to make inroads outside towns. Overall turnout was low.
Chamisa accused the ruling Zanu-PF of using underhand tactics. Party officials said traditional leaders in rural constituencies intimidated voters by forcing them to register names in a local database before voting. Electoral officials denied the accusations.
“Had it not been for rigging and other shenanigans particularly in the countryside we would be talking about [winning] almost 26 out of 28 [constituencies] but … the citizens are clear and have made a bold statement,” Chamisa said.
Electoral and ruling party officials denied the allegations.
Though campaigning in 2018 was relatively peaceful, the polls were followed by a wave of repression with soldiers shooting civilians in central Harare and hundreds of arbitrary detentions.
In campaigning for last weekend’s byelections, CCC supporters were teargassed or assaulted by police, several were arrested and one killed. The party was forced to obtain court orders to allow rallies to go ahead after authorities claimed there were insufficient police officers to provide security.
Independent observer groups such as the Zimbabwe Election Support Network (Zesn) said some candidates’ conduct amounted to vote buying, including giving out food to voters.
“The election day was peaceful but with concerns of community coercion,” Zesn said in a statement.
In the southern city of Bulawayo, ruling party officials distributed sacks of maize flour before the vote, residents told the Guardian.
Human rights organisations have accused the ruling party of encouraging violence. On 26 February, Zimbabwe’s vice-president, Constantino Chiwenga, said the ruling Zanu-PF party would “crush the (opposition) like lice under a stone.”
A day later, a gang of unidentified men entered the centre of Kwekwe, a town 200km from Harare and a key constituency, where they attacked CCC supporters on their way to a rally.
Around 20 people were injured with bottles, iron bars, spears and bricks. Mboneni Ncube, a 30-year-old man and opposition supporter died after being stabbed.
Five suspects have been arrested and charged with murder.
Amnesty said the attack appeared to be pre-meditated to intimidate political opposition.
After the Covid restrictions were lifted in September, Chamisa began a “meet-the-people” tour.
In Masvingo province and other places, Zanu-PF supporters damaged vehicles and beat villagers who came out to support him.
On at least one occasion, supporters were forced to publicly denounce him and on 20 October, Chamisa was shot at in Manicaland province, Amnesty said.
Another opposition supporter died in November after being beaten in Gutu by suspected Zanu-PF supporters.
His wife and other relatives were charged with defamation after they accused ruling party members of being responsible.
Before the polls, Zanu-PF officials said they were targeting the urban vote.
Party spokesperson accused the opposition of “neglect, feckless maladministration, screaming corruption, and putrid decay”.
“The electoral jury is out. Come the 2023 … elections, Zanu-PF envisages an electoral tsunami that will drown the foreign spawned opposition”,Mutswvangwa said in a statement broadcast by state-controlled media.
In the run-up to the vote, Mnangagwa threatened to suspend the work of all NGOs – even those working to protect millions from malnutrition.
Mugabe banned NGOs when he feared defeat in polls, and frequently accused aid agencies of conspiring with the opposition and usually unidentified foreigners.
After Mugabe secured victory in the contested and violent election of 2008, he lifted the ban on the aid groups.
The current government aim to bring in new laws that will make NGOs disclose their source of funding and ban them from activities deemed “political”.
The government say that the measure aims to target “money-laundering and terrorist funding”.
“We can do without NGOs. I will remove them from this country, I will chase them away,” Mnangagwa said before the bye-lections.
Some fear a ban on aid agencies would lead to drastic cuts in humanitarian assistance, estimated at $800m a year.
Blessing Vava, head of a local democracy and governance group, Crisis Coalition, said Mnangagwa was seeking “to entrench a one-party state and a dictatorship where the government does not want to be accountable”.
No opposition has won an election and formed the government in the former British colony since independence in 1980.
Chamisa has complained of a flawed voters’ roll and has accused the Zimbabwe Electoral Commission (Zec) of transferring voters from one constituency to the other without their knowledge.
“Yes, we had a landslide, but those issues are still there … Zanu-PF do not believe in a free vote,” Chamisa said. – The Guardian

 Slider3 years ago
Slider3 years ago
 National4 years ago
National4 years ago
 Tourism and Environment4 years ago
Tourism and Environment4 years ago
 Special reports4 years ago
Special reports4 years ago
 Opinion4 years ago
Opinion4 years ago
 National4 years ago
National4 years ago
 National3 years ago
National3 years ago
 National3 years ago
National3 years ago