BY FRANK CHIKOWORE
The UN Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organisation (Unesco) is warning that Victoria Falls could lose World Heritage Site status if the Zimbabwean and Zambian governments proceed with development plans near one of the Seven Natural Wonders of the World.
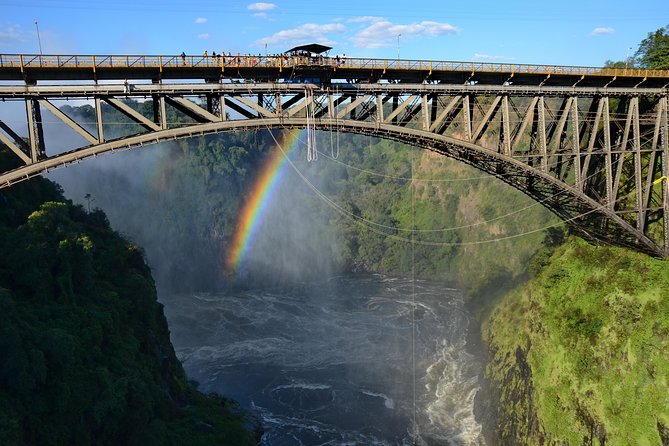
Victoria Falls, on the Zambezi River, is on the border between Zambia and Zimbabwe and is the world’s largest sheet of falling water, spanning 1.7km and dropping 108m into a gorge.
It is the main tourist attraction for both countries, where visitors can enjoy sightseeing, bungee jumping, white-water rafting, boat cruises, game viewing and the world-famous Flight of Angels.
Plans are at an advanced stage to build a hydroelectric power station, a 300-bed hotel complex and a golf course near the falls, according to a Unesco report.
The power plant proposal comes as Zimbabwe is facing an acute shortage of electricity that has seen the Zimbabwe Electricity Supply Authority (Zesa) introduce power cuts.
Zesa is also struggling to pay at least $6 million a month for electricity it gets from Zambia – which has achieved an electricity generation surplus of 1,156MW since a new power plant was built in the north of the country.
Victor Mapani, managing director of Zambia’s power utility Zesco, has said the country’s power surplus is available for trade in the southern African region, within the interconnected power network.
President Emmerson Mnangagwa announced this week that he planned to engage his Zambian and Mozambican counterparts with a view to solving his country’s power deficit.
Some commentators say building a power plant near Victoria Falls will ease Zimbabwe’s electricity problems, but activists like Farai Maguwu, director of the Centre for Natural Resource Governance, say it will have a negative impact on Zimbabwe’s already ailing economy.
The country’s month-on-month inflation rate hit 25.6 percent in July.
A recent Zimbabwe cabinet report said tourism contributes at least US$1.9 billion to gross domestic product annually, and projected it could hit a $5 billion target by 2025.
However, Maguwu said projections might not be met if the developments go ahead.
“Victoria Falls is one of the natural wonders created by God. It is important that the falls are preserved because that is what attracts tourists,” Maguwu said.
“The Zimbabwean government should not be seen to be pushing away foreign tourists.
“It is not surprising that some top government officials are seeing an opportunity to make money through these commercial projects.”
Zimbabwe’s minister of environment and tourism, Mangaliso Ndlovu, declined to comment on “the Unesco matter”.
Home Affairs and Heritage minister Kazembe Kazembe said he was not aware of any proposed commercial activities near Victoria Falls.
“I am not aware of the project,” Kazembe said.
“If indeed the project is on the cards I trust your concerns will have been considered during the design.
“The heritage will certainly be protected.”
Environment and Management Agency communications officer Joyce Chapungu said: “We have not received any documentation for these proposed developmental projects to enable us to do any environmental impact assessment exercise in order to ascertain how these projects would affect the concerned district.”
Coalition for Market and Liberal Solutions director Rejoice Ngwenya urged Zambian and Zimbabwean authorities to move the projects elsewhere.
“It is important for both Zambia and Zimbabwe to respect the views and expertise of Unesco,” Ngwenya said.
“These governments can do these projects at least 40km from the heritage site.
“It is not in dispute that construction of a hotel, power plant and golf course will create jobs, but they must look at the bigger picture.”
Labour Economic Research Institute of Zimbabwe economist Prosper Chitambara said the projects would not hit the economy.
“Tourists come to see the waterfall and there is no tourist who would want to go to a place where there is no electricity and enough accommodation,” Chitambara said.
“The setting up of a hotel and a power plant will help in revamping facilities in the resort town.” – Daily Maverick

 Slider3 years ago
Slider3 years ago
 National4 years ago
National4 years ago
 Tourism and Environment4 years ago
Tourism and Environment4 years ago
 Special reports4 years ago
Special reports4 years ago
 Opinion4 years ago
Opinion4 years ago
 National4 years ago
National4 years ago
 National3 years ago
National3 years ago
 National3 years ago
National3 years ago