BY NOKUTHABA DLAMINI
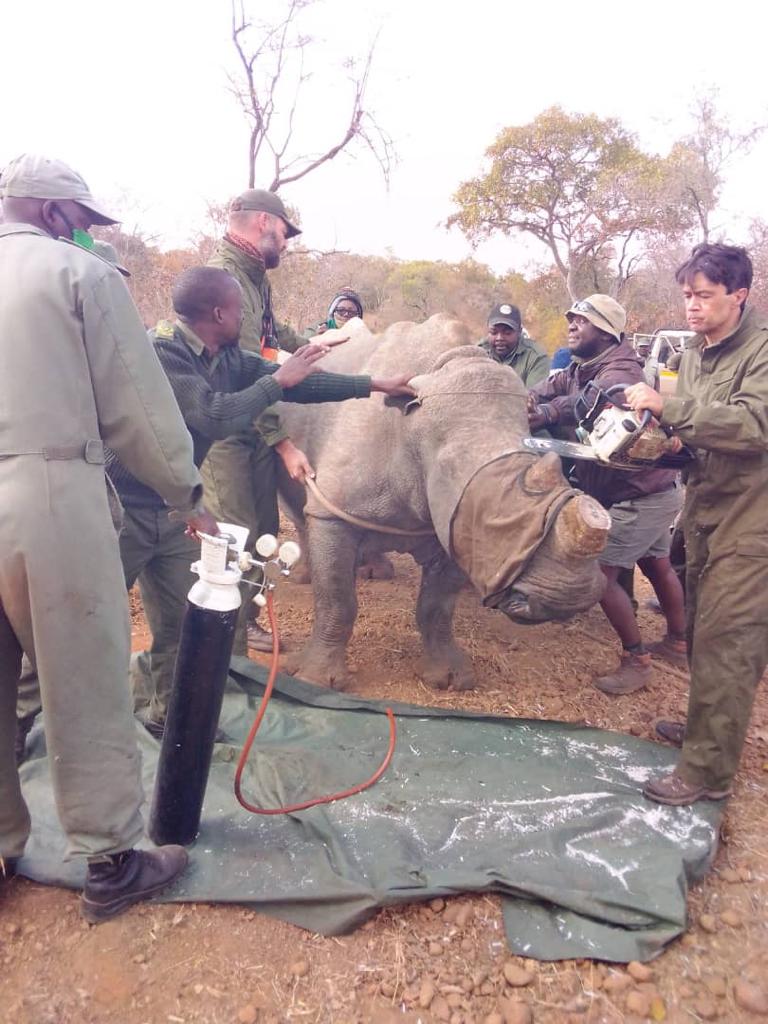
Columbus Chaitezvi became animated as he narrated a near death experience with a black rhino in Zimbabwe’s Save Valley Conservancy while doing something conservationists believe is the antidote for the high levels of poaching of the endangered species.
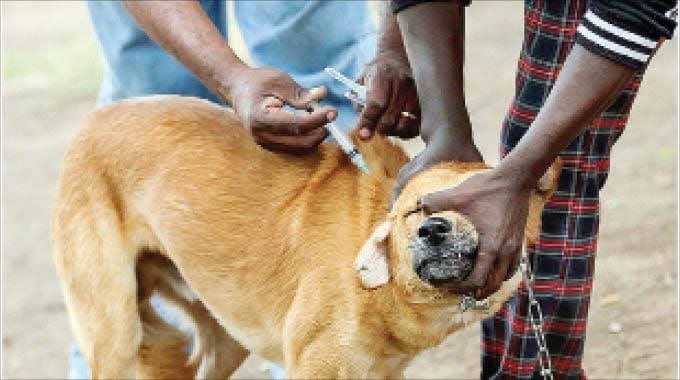
Chaitezvi, a senior veterinary officer at the Zimbabwe Parks and Wildlife Management Authority (Zimparks), is part of a team spearheading a project to dehorn the remaining rhinos in the country’s game reserves in order to protect them from poachers.
Conservationists see rhino dehorning as a temporary measure to prevent the killing of the animals for their horns by poachers.
Dehorning is a continuous process as the horn regrows after removal.
Rhinos are targeted by poachers because their horns are in high demand, especially in Asia.
Zimbabwe now has over 1000 rhinos after poachers decimated their population three decades ago and Zimparks believes dehorning is one of the best ways to protect the animals.
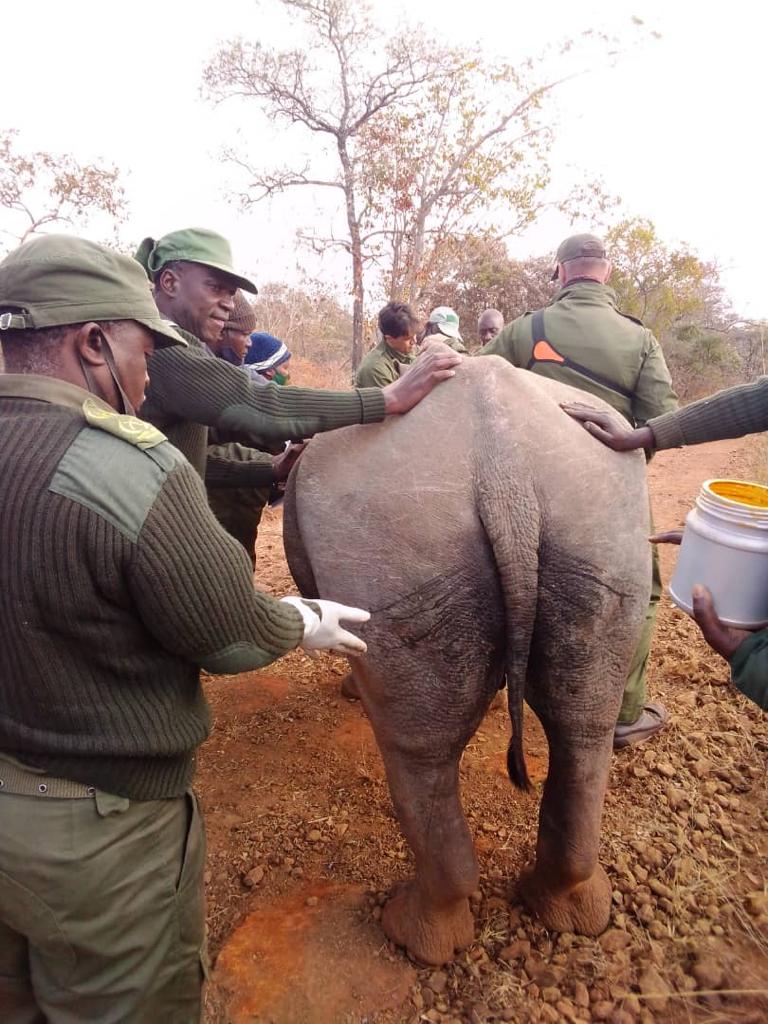

Chaitezvi described the dehorning exercise as a dangerous, but worthwhile exercise because of the benefits to the country’s wildlife and tourism industry.
He described the 2019 Save Valley near death experience as part of the hazards of the mission that has seen them dehorning rhinos across the country, which at times comes at the cost of human lives.
“We were at the Save Valley when one of my colleagues who was assisting with the operation said he assumed that the rhino was struggling to breathe and decided to inject it with a reversal drug without notifying us,” Chaitezvi said.
“As I was still doing the work I suddenly saw the rhino opening its eyes and within no time it was up and ready to attack.
“I immediately took off and it was just a second behind me and using my survival skills I decided to take a sharp turn in front of it because rhinos struggle with sharp turns.
“So it passed through and that’s how I was lucky to make it to the next minute.”
His team has several tales to tell about dangers posed by the exercise, but passion and dedication has ensured that they keep their eyes on the ball.
Early this month, a Zimparks ranger who was part of the annual dehorning programme, suffered serious injuries after he was attacked by a black rhino at the Matopos National Park in Matabeleland South.
“We come across these life-threatening encounters on several occasions because we are hardly equipped with necessary resources, but we remain dedicated to fight for these rhinos and save them from extinction,” Chaitezvi said.
“One of my colleagues Ray Makwehe (now deceased) got seriously injured by the same dangerous black rhino type as he was doing the same job and he sustained serious injuries on his thigh and permanently lost one of his fingers too.
“But that did not deter him because he was involved in another helicopter crash that he survived while doing conservation work.
“The tales are many, but we lighten up about them when the work has been fulfilled because ours is to conserve and fight wildlife crimes, and our partners have helped us to slow down poaching of the rhinos over the years inside our national parks which is Lake Kyle Recreational Park, Chivero, Hwange, Matopos and Chipinge.”
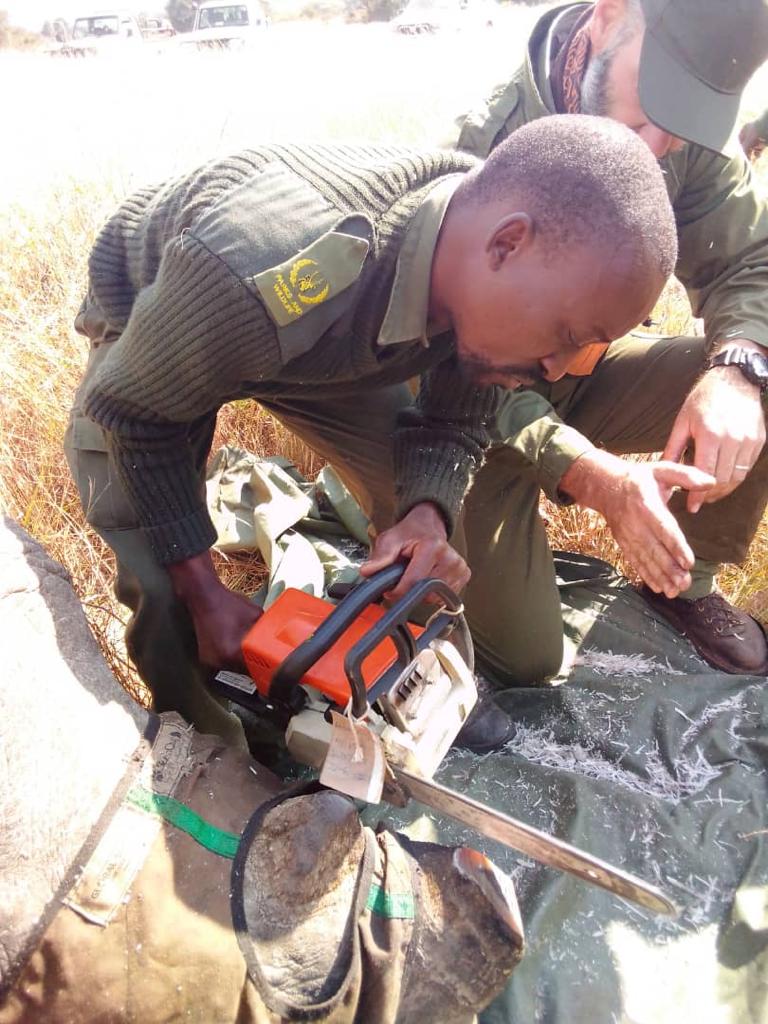

He added: “Before the Covid-19 pandemic, we had serious poaching cases happening at one of our private run game Bubye Valley Conservancy and we took action by sending more security and poaching has drastically reduced there.”
Zimparks national rhino coordinator Diana Marewangepo-Chasara said the dehorning exercise targeted mature rhinos to make them unattractive for poachers.
“Dehorning is done to reduce rewards for poachers,” Marewangepo-Chasara said.
“It reduces the amount of horn that the poacher can obtain by killing a rhino and, therefore, the payment that he receives from the sale of the horn.”
Zimparks, however, says it is struggling to implement the dehorning exercise due to financial constraints.
Money is needed to buy drugs to sedate the rhinos before they are dehorned, for transport for the dehorning teams and to buy equipment for rangers.
“The dehorning exercise is extremely costly and as such the biggest challenge to date has been the funding,” Chaitezvi added.
“Zimparks is facing serious financial challenges, which have resulted mainly from effects of the Covid-19 pandemic as well as the country’s economic challenges and financial constraints also lead to manpower shortages and lack of adequate resources to effectively carry out vital operations.”
Zimparks does not have its own helicopter or fixed wing plane, which means that the Authority has to outsource the services at a high cost.
At times, the dehorning teams have to track the rhinos on foot, which could be dangerous and time consuming, Chaitezvi revealed.
“We try to use what we have, like in Chivero National Park, we were using Land Cruisers while we also track them on foot which can take the whole day to find one,” he said.
“The drugs are expensive and also the expertise is limited as we are only three instead of four because of economic challenges looking at the effects of Covid-19, but our goal remains the same, (to protect rhinos).”
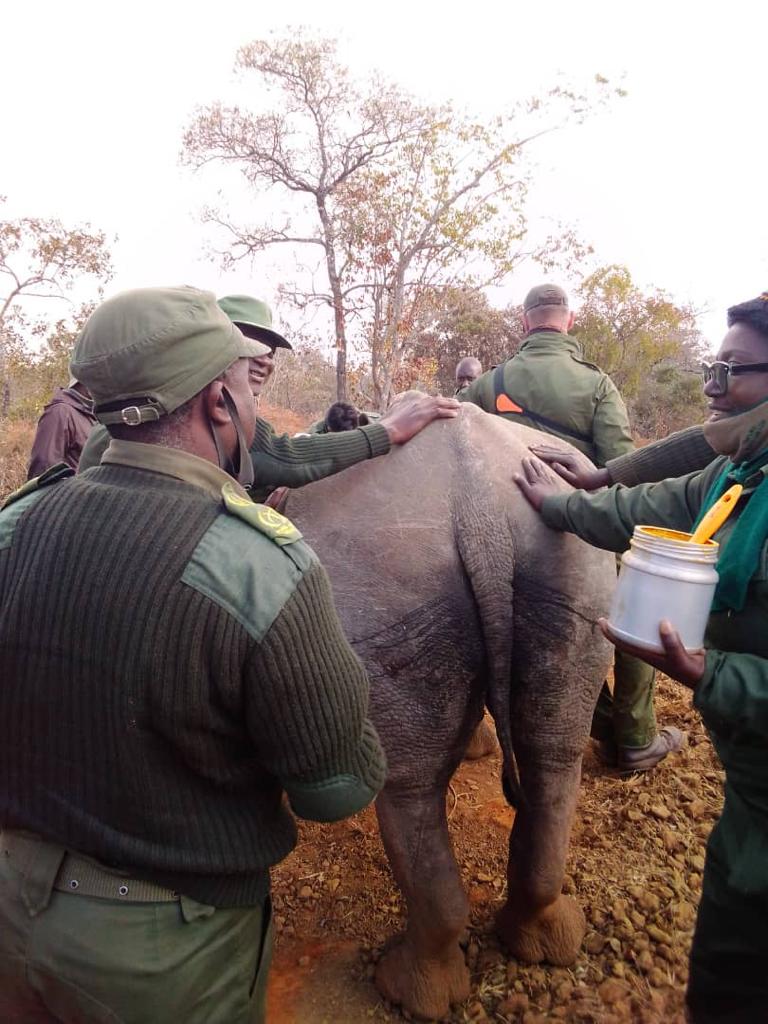

He said on average, the process of dehorning costs US$2000 per rhino which covers for immobilisation drugs, darting, reversal, oxygen and medication.
“We use etofine opioids drugs, which are costly because they are administered in pairs and this also includes the reversal after the process of dehorning has been done, which costs about US$ 800,” he said.
“On top of that we the dehorning process requires oxygen tanks, dressing kits, antibiotics, pain killers and monitoring gadget for operations and that goes up to US$2000 per rhino and that is why we have had to rely on donor funding to cover one park per year.”
Zimbabwe in May hosted the Africa Elephant Summit in Hwange, which sought to explore ways of promoting sustainable conservation in the region and funding of conservation efforts was topical.
The summit pushed for the liberalisation of trade in wildlife products by developing a viable instrument which will enable African elephant range states to sell ivory stockpiles to raise funds for conservation.
The Hwange Declaration, signed at the end of the summit, made a clarion call for the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora not to interfere with domestic trade, state sovereignty, and their rights to sustainable use of wildlife.
It will be tabled at the International Wildlife Conference to be held in Panama in November.
If the lobby succeeds, Zimparks can sell its huge stockpiles of ivory to fund conservation efforts such as the dehorning of rhinos, which conservations believe has been instrumental in bringing down cases of poaching across the globe.
According to a new report by International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN, globally the overall rhino poaching rates have declined since 2018.
Trade data suggests the annual estimate of rhino horns entering illegal trade markets have also declined since 2013.
The report says rhino poaching rates in Africa have continued to decline from a peak of 5.3% of the total population in 2015 to 2.3% in 2021.
It added that at least 2,707 rhinos were poached across Africa between 2018 and 2021. – The Standard

 Slider3 years ago
Slider3 years ago
 National4 years ago
National4 years ago
 Tourism and Environment4 years ago
Tourism and Environment4 years ago
 Special reports4 years ago
Special reports4 years ago
 Opinion4 years ago
Opinion4 years ago
 National4 years ago
National4 years ago
 National3 years ago
National3 years ago
 National3 years ago
National3 years ago