BY NOKUTHABA DLAMINI
Bongani Ndlovu, a Zanu PF councillor in Matabeleland North’s Bubi district holds the unenviable record of registering the least number of voters in the March 26 parliamentary and local government elections.
Only 27 people voted for Ndlovu to represent Bubi’s ward six, the official tally of the council by elections released by the Zimbabwe Electoral Commission (ZEC) showed.
His closest rival Benjie Mpofu of the newly formed Citizens Coalition for Change (CCC) garnered a meagre nine votes.
According to ZEC, ward six had over 500 registered voters when the by-elections were held and the number of people who turned up to vote for the new council showed a serious voter apathy.
In an almost similar situation, only 209 people out of a possible 709 in Victoria Falls turned out to elect the new councillor for war one.
A statistical analysis of the voter turnout in the March 26 by elections by the Zimbabwe Independent in collaboration with the Information for Development Trust (IDT) –a non-profit organisation that supports journalists in Zimbabwe and in the region to investigate issues of corruption in the public sector and bad governance –showed that the Bubi and Victoria Falls scenario demonstrated a national trend of massive voter apathy in the by-elections.
 There were 28 parliament seats and 122 local government vacancies that were up for grabs as the county held its first by-elections since the 2018 polls following a ban on polls due to the outbreak of Covid-19.
There were 28 parliament seats and 122 local government vacancies that were up for grabs as the county held its first by-elections since the 2018 polls following a ban on polls due to the outbreak of Covid-19.
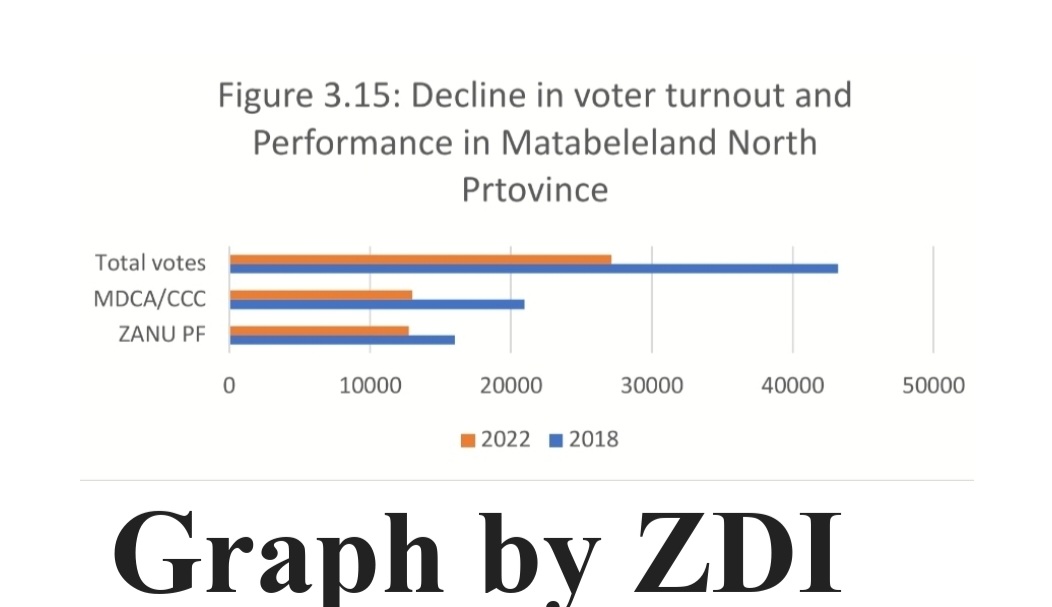
Analysis of the by-election results backed by research by the Zimbabwe Democracy Institute (ZDI) showed that there was a 37 percent decline in the number of people that turned out to vote in the by-elections in Matabeleland North compared to those that cast their ballots in the 2018 polls.
Binga North was the only constituency in the province where there was a high voter turnout after 20 000 people cast their ballots to choose the new MP.
The ZDI analysis showed that the opposition recorded a bigger decline in the number of people who voted for its candidates as the CCC candidates got 38 percent less votes compared to what the MDC Alliance garnered in the 2018 elections.
MDC Alliance was the country’s largest opposition party in the 2018 polls, but was eclipsed by the three-month-old CCC in the by-elections.
Zanu PF saw a 21 percent decline in the number of voters who backed its candidates in the by-elections compared to the previous elections.
“Zanu PF improved its performance in Matabeleland North during the 2022 by-elections from the 2018 elections as shown by a 10% increase from 37% in 2018 to 47% in 2022 whereas CCC remained static (48%) between 2018 and 2022,” ZDI said.
“The winning margin of the opposition in these areas is decreasing.”
The research showed that voter apathy characterised the by-elections in all the country’s 10 provinces with Harare registering a staggering 66 percent decline in voter turnout and Bulawayo 75 percent compared to the 2018 elections.
Voter turnout in the general elections, which were the first since the ouster of long-time ruler Robert Mugabe in a military coup a year earlier, was 75 percent.
Carol Mubita, a Matabeleland North based election observer, said worsening voter apathy showed that people were losing faith in political leaders given the state of the economy and their failure to deliver on election promises.
“This is why in Bubi only 37 people voted. I was there before the by-elections and the mood was that even if they vote they will remain stuck in poverty,” Mubita said.
“Politicians have failed the people they represent, and the unemployment levels continue going up.”
Pedzisayi Ruhanya, a Harare based academic and political analyst, said the reasons why Zimbabweans were not turning out to vote ranged from interference in electoral processes by security forces, waning confidence in ZEC and the opposition’s limited mobilisation capabilities.
Ruhanya cited political violence blamed on the ruling Zanu PF ahead of the March by-elections and moves by security forces to stop the opposition from campaigning for the poor turnout.
“You find them through Zanu PF storming a CCC rally and as such, one individual was killed in Kwekwe,” he said.
“Then you see that in Gokwe again where we saw the deployment of violent police with water cannons and again in Marondera where the police stopped a meeting of the CCC.
“So, there is an unholy alliance used by Zanu PF as the security apparatus in which the military and police work as the commissariat of Zanu during the elections
“When you look at voter turnout that affected the numbers because these people are intimidating the electorate.”
Wes Beal, a member of Pachedu, a group that has been exposing the poor state of the voters roll and other electoral malpractices on social media, believes that although questions around ZEC’s credibility could result in people losing confidence in the electoral system, voter turnout during by-elections is always very low compared to general elections.
“ZEC hasn’t released the number of votes cast (to date), but that said, turnout is always lower in by-elections compared to the national elections the world over,” Beal said.
There were widespread reports of people that were turned away from polling stations because they had been moved to different stations without their knowledge.
Zimbabwe’s voter roll is polling station based. ZEC was also accused of surreptitiously moving polling stations.
Ruhanya said ZEC’s conduct disenfranchised voters.
Beal said people also lose confidence in the electoral system because of poor performances by elected representatives.
Zimbabwe will hold general elections next year and ZEC is already working on the delimitation of constituencies.

 Slider3 years ago
Slider3 years ago
 National4 years ago
National4 years ago
 Tourism and Environment4 years ago
Tourism and Environment4 years ago
 Opinion4 years ago
Opinion4 years ago
 Special reports4 years ago
Special reports4 years ago
 National4 years ago
National4 years ago
 National3 years ago
National3 years ago
 National3 years ago
National3 years ago

 There were 28 parliament seats and 122 local government vacancies that were up for grabs as the county held its first by-elections since the 2018 polls following a ban on polls due to the outbreak of Covid-19.
There were 28 parliament seats and 122 local government vacancies that were up for grabs as the county held its first by-elections since the 2018 polls following a ban on polls due to the outbreak of Covid-19.



