BY NOKUTHABA DLAMINI
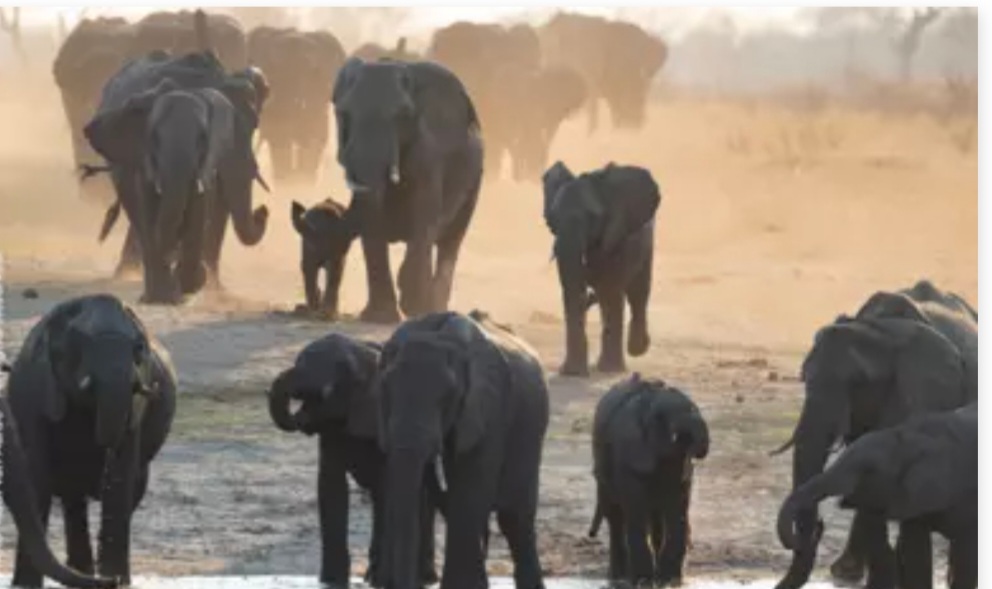
Hwange National Park, once a favourite hunting ground for poachers, has not lost an elephant to the illegal hunters for the past two years largely because of partnerships between the Zimbabwe Parks and Wildlife Management Authority (Zimparks) and non-governmental organisations.
In 2013, over 300 elephants were killed by poachers at the country’s largest game reserve as the menace reached its peak.
Poachers, who included villagers from rural outposts such as Tsholotsho and Hwange used cyanide to kill the elephants for their ivory.
One of the major organisations that have joined hands with Zimparks to protect the animals in Hwange is Bhejani Trust, which also operates at the Zambezi National Park and Kazuma Pan National Park in Matabeleland North.
Bhejane Trust director Trevor Lane said the last elephant poaching incident at the Hwange National Park was in 2020 and he attributed the of the anti-poaching activities to the partnerships between Zimparks and conservation groups.
“Efforts by (Zimparks) and what we do differently to promote conservation in the region has positively impacted on conservation of our wildlife, especially elephants which frequently strayed out of national parks into communal areas to search for food and water,” Lane said.
“As an organisation ours is to ensure that our wildlife has adequate water supply because generally where we operate natural water is drying up fast during the summer and the pressure of elephants all coming together.
“We are faced with a challenge of keeping up with the demand in order for us to keep them inside the parks.
“Every year we have managed to put in a few more water pumps. We are trying to put in more pumps into the back area of Robins Camp because while there’s natural water, there’s a good population of elephants.
“But once that dries up the elephants are all forced to go forward to the existing pumps, which adds to the pressure. Some end up straying outside, leading to human wildlife conflict situations, that’s why we want to add more from the existing 49 to drive them back into the park.”
The organisation pumps one million litres of water per day, which is consumed by approximately 16 000 elephants out of the 44 000 found in the Hwange National Park
Another fruitful partnership for Zimparks is with the international Fund for Animal Welfare (IFAW), which recently set up a new ranger station in the Makona area of Hwange National Park to strengthen the fight against poachers.
IFAW said the ranger station will also help the communities living near the park, who have suffered from elephants and other large herbivores destroying their crops and predators killing their livestock.
“When complete, the camp will be home to 56 rangers and their families who will live and work there,” IFAW said in a statement.
“Comfortable housing, equipped with electricity and running water, is being built for junior rangers and senior staff, and a recreation centre is under construction.
The operations centre is already in use and set up with a landscape-wide VHF radio network—vital communications equipment that connects rangers and improves responses to incidents of poaching.”
IFAW said before the camp was constructed responses to poaching incidents and reaction to reports on problem animals were slow, with rangers being deployed from Hwange Main Camp, some 95 kilometres away and enduring a terrible road snaking through the sticky Kalahari sands.
Augustine Gomba, Zimparks’ wildlife cfficer based at Hwange Main Camp, said before the road was developed, driving to Makona was a nightmare.
“The sandy soils and the rugged nature of the road meant that on average the trip to Makona would take a grueling four hours at least,” Gomba said.
A key achievement of the IFAW-Zimparks agreement was the improvement of the road, cutting a journey that could take up to four hours down to less than two.
The park is nestled on the edge of the Kalahari Desert and is home to some of Africa’s most iconic species.
Being largely flat and dominated by scattered woodlands of teak trees, it was an easy target for poachers.
“The new ranger station will prevent poachers from entering Hwange National Park into the future, allowing the park’s elephants and other wildlife to continue to flourish,” IFAW said.
Zimparks struggles to fund conservation efforts due to poor funding. – The Standard

 Slider3 years ago
Slider3 years ago
 National4 years ago
National4 years ago
 Tourism and Environment4 years ago
Tourism and Environment4 years ago
 Special reports4 years ago
Special reports4 years ago
 Opinion4 years ago
Opinion4 years ago
 National4 years ago
National4 years ago
 National3 years ago
National3 years ago
 National3 years ago
National3 years ago