BY FORTUNE MOYO
Sithethile Nkomo’s children are too young to understand why their mother no longer sends them off to school with the usual bread and butter in their lunchboxes.
Nkomo’s daughters, ages three and five, are used to eating bread for breakfast, then again for lunch at school, and as a snack when they return home in the afternoon.
Now the single mom packs green mealies, or corn on the cob, and amakhomane, a protein-rich legume with a nutty flavour.
While this provides a healthy alternative, her children miss the bread they are used to eating every day, and Nkomo worries they are not getting all the essential nutrients.
“Bread has become expensive, and the price keeps increasing,” says Nkomo, who works in a grocery store selling the bread she can no longer afford to buy every day.
“When I do not have flour to bake buns, I cook mealies and amakhomane.”
Already recovering from a hike in food prices and limited access to everyday staples due to transportation difficulties during the coronavirus pandemic, Zimbabweans are now suffering the effects of the Ukraine-Russia conflict, which has halted wheat exports out of two countries once ranked among the world’s biggest exporters of the grain.
The catastrophic strain on the supply chain is forcing many to reduce their food intake in a country where 2.4 million people living in urban areas had limited food access prior to the conflict.
The high demand for bread in Zimbabwe has elevated wheat to the second most important crop in the land-locked country, after maize, or corn, with more than 400,000 metric tons of wheat consumed each year.
Zimbabwe was once considered the breadbasket of Africa for its rich agricultural landscape, but a recent rise in its dependency on imported goods has slowly erased the country’s self-sufficiency.
Now authorities are considering ways to bolster its production of food, particularly wheat.
In 2019, Hilal Elver, then the United Nations special rapporteur on the right to food, urged the government to “take the necessary measures to reduce the country’s dependence on imported food … to ensure the country’s self-sufficiency” after finding that more than 60 percent of the population was food insecure.
At the time, the UN said Zimbabwe was on the “brink of [a] man-made starvation,” with Elver citing high unemployment, recurrent droughts and severe price instabilities as factors in the crisis.
Three years later, the conflict in Ukraine has pushed prices beyond affordability.
Nkomo used to buy a loaf of bread, sometimes two, every day to feed her family, but with the price more than doubling in recent months, she can now buy a loaf only two, sometimes three, times a week.
The energetic mom whose smile never fades works 16-hour days at the grocery store and supplements her income with a hairdressing business she runs from her home, providing her with a monthly income of 20,000 Zimbabwean dollars (ZWL) to 22,000 ZWL ($55 to $60). Buying a loaf every day would consume half her monthly income.
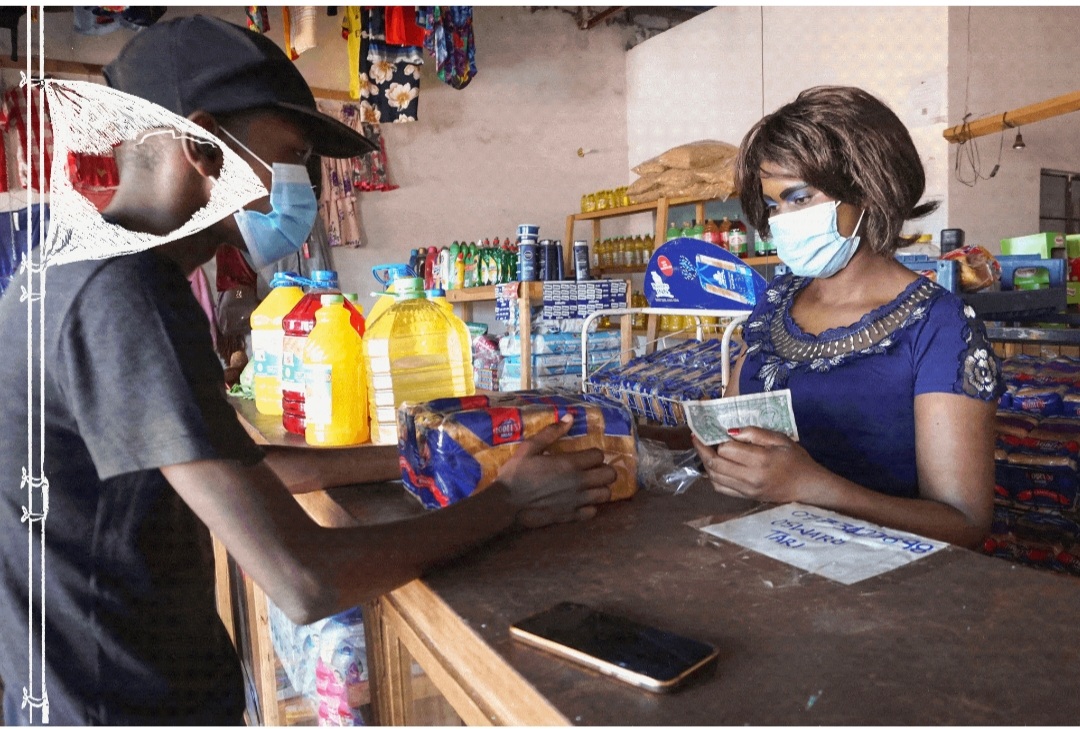
She would typically sell 40 to 50 loaves each day at the grocery store, but lately only half that number are leaving the shelves. Store owner Oswald Kasi says bread was one of his fastest moving products.
“The increase in the cost of bread and flour has affected my sales,” says Kasi, who has reduced the number of loaves he orders due to dwindling demand.
Families are forced to seek cheaper alternatives to replace their daily bread, and they’re not always popular.
“Although my children prefer bread, mealies and amakhomane last two to three days while a loaf of bread does not last 24 hours,” says Nkomo, who now favors buying a two kilogramme (4.4-pound) bag of flour for US$2 and making buns, a cheaper option that allows her to stretch the bread supply for her family.
Flour-based foods provide essential nutrition.
Fortifying wheat flour with vitamins A and B, folic acid, iron and zinc became compulsory in Zimbabwe in 2016 to address major vitamin deficiencies found in children ages six months to five years.
Fungai Mvura, Hwange medical officer under the Ministry of Health and Child Care, says the absence or reduction of bread in people’s diets will have consequences.
“Bread is part of carbohydrates, which is the main source of energy,” Mvura says.
“In the long run, cutting down on such products may lead to weight loss, not in the form of fats but loss of calories found in carbohydrates.”
Ukraine is Zimbabwe’s third-biggest supplier of wheat behind South Africa and Latvia, but the stress on the supply chain is forcing officials to consider other options.
“Zimbabwe imports about 130,000 tons of wheat every year to cover the deficit,” says Tafadzwa Musarara, chairman of the Grain Millers Association of Zimbabwe.
“The Russia-Ukraine war has worsened the situation, and there is a need for us to come up with ways of being self-sufficient.”
Anxious Jongwe Masuka, the minister of lands, agriculture, fisheries, water, climate and rural resettlement, says the government is taking steps toward self-sufficiency.
“This year our goal is to make sure that we increase the number of farmers planting wheat and also increase hectarage,” Masuka says.
“We may need around 75,000 hectares to have enough wheat in the country.”
He says he believes this number is achievable as the country has 65,000 hectares available to grow wheat.
The government confirmed its 75,000-hectare target in a statement released in March announcing an investment of more than $9 million for its Presidential Winter Wheat Programme, which includes providing wheat seeds, fertilizers and machinery for farmers to help the government achieve its goal.
Michael Nyabadza, who for the past five years has grown wheat in Makoni, a district in northeastern Zimbabwe, is one farmer who has benefited from this programme.
“I started with 40 hectares, and I increased to 150 hectares last year, which gives me between seven and eight tonnes of wheat,” says the 66-year-old farmer, who received government assistance in the form of additional seeds and fertilizer to increase his yield.
Nyabadza believes it’s possible for Zimbabwe to be self-sufficient in wheat production, but this goal is not dependent only on a cash injection.
“This year, we got too much rain late into the season, so our maize did not dry early enough for us to remove and free the land for more wheat space,” he says.
“That is how weather has disrupted cropping operations.”
Meanwhile, Zimbabweans like Nkomo can only wait and hope the government’s initiatives pay off.
Each day Nkomo worries her children are not getting the sustenance they need to thrive.“I feel like I am depriving them of something they are used to,” she says. “It’s an important part of their diet.” – Global Press Journal


 Slider3 years ago
Slider3 years ago
 National4 years ago
National4 years ago
 Tourism and Environment4 years ago
Tourism and Environment4 years ago
 Opinion4 years ago
Opinion4 years ago
 Special reports4 years ago
Special reports4 years ago
 National4 years ago
National4 years ago
 National3 years ago
National3 years ago
 National3 years ago
National3 years ago